Maritime 2.0
Maritime 2.0 was introduced as an evolution of our existing REST APIs in 2020, as a response to the challenges in increasing data volume and quality. Maritime 2.0 was developed to be scalable.
Spire chose to leverage GraphQL technology instead of REST for this newly enhanced service as GraphQL offers the client the ability to describe the data and get exactly the data that is needed through the use of queries.
Ultimately, Spire Maritime 2.0 delivers state of the art vessel data infrastructure that enables customers to unlock the value of the data and provide access to vessel data from various data sources, such as AIS, with more sources such as Vessel Characteristics and routing services to come in the future.

Get started now
Download our open source Postman collection, drop in your access token and you will be making Maritime 2.0 API calls in seconds.
Don’t have a token yet? Request a trial
GraphQL Overview
GraphQL is an API technology developed by Facebook in 2015 and adopted over the world by top technological companies. In this guide we will show the benefits of GraphQL as a technology and also provide an overview of some powerful and advanced features of GraphQL query syntax. After this article you will understand what benefits GraphQL gives you as a customer as well as be able to use advanced features of GraphQL to power your queries.
GraphQL is an API technology which allows allows customers to query API in the requests. Contrary to REST where specific endpoints are used to identify the resource, the GraphQL exposes a single endpoint with a global GraphQL schema. GraphQL schema defines what is possible to query and underlying data types. Customers are sending queries against the schema to the GraphQL server as a POST request. You can query whatever you want using a single API endpoint (but according to the granted permissions) and the shape of the response will match the shape of the query.
For Spire, as data provider, the GraphQL gives following benefits:
- Integrated API – in one query you can query multiple data sources at once. For example, querying for the vessel you can get vessel characteristics, destination port, predicted route and so on. Such kind of API is impossible to create with REST approach.
- Single API endpoint – single endpoint
api.spire.com/graphqlwhere all the operations are available. Integrating any new feature into GraphQL should be straightforward for Spire as well as for our customers. - Flexibility – in the long term GraphQL allows more flexibility than REST. At first, GraphQL supports queries, mutations, subscriptions out of the box, where subscriptions are really promising for the Maritime domain. Second, GraphQL schema could be evolved in a way to integrate various data sources.
- Documentation – GraphQL schema serves as live documentation for our API.
For you, as a customer, GraphQL gives a following benefits:
- Query only what you need – as a customer you can focus only on a subset of the data you need therefore reducing the amount of transferred data which will lead to better performance.
- Parallel queries – you might sent a query with a multiple root fields which will be resolved in parallel.
- Typesafe queries – all queries are validated against GraphQL schema and safe to execute.
- API Playground – at api.spire.com/graphql there is a GraphQL playground available where you can play and prototype query of any complexity.
GraphQL represents a massive leap forward for API development. Type safety, introspection, generated documentation, and predictable responses benefit both the data provider and customers of the API platform.
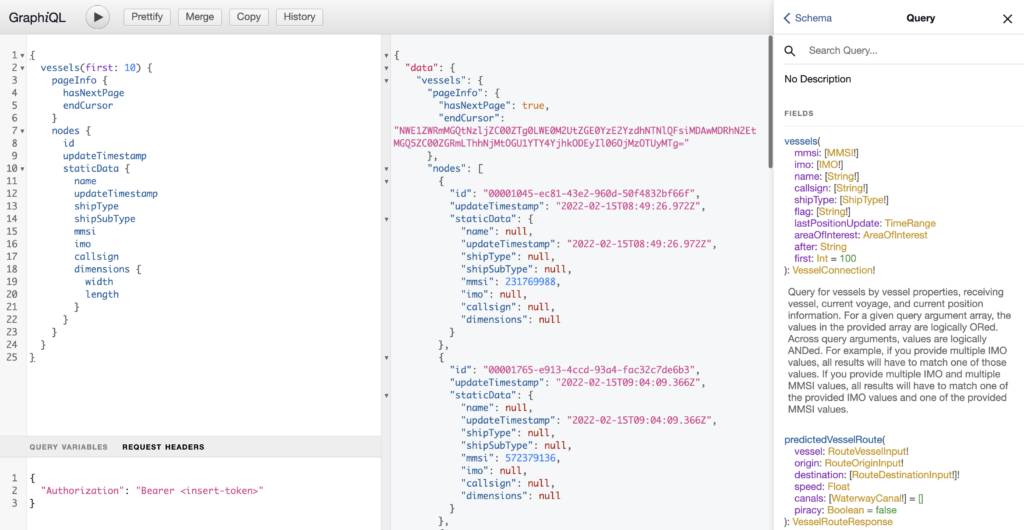
GraphQL playground
All samples queries can be executed in our GraphQL playground, where you also have access to interactive Docs and Schema pages.
Don’t have a token yet? Request a trial
Writing a query
To access the data through the Spire Maritime 2.0 API, you will need to execute a GraphQL query.
This query essentially asks for specific fields on one or more objects; in other words, a GraphQL query describes the shape of your data “graph”.
A query is generally structured based on the following outline:
query {
rootQuery(
argument1:<value>
...
argumentN:<value>
) {
outputField1
...
outputFieldN
}
}Video tutorial: Running your first GraphQL query
query FirstQuery {
vessels(imo: [9538907, 9726413]) {
nodes {
staticData {
name
mmsi
imo
}
lastPositionUpdate {
accuracy
collectionType
course
timestamp
updateTimestamp
}
currentVoyage {
draught
}
}
}
}This is how you put your token in Playground:
{
"Authorization": "Bearer <your token>”
}Syntax
Named and unnamed queries
The basic GraphQL query to get mmsi and name for first 3 vessels might look like:
{
vessels(first: 3) {
nodes {
staticData {
mmsi
name
}
}
}
}This is so-called unnamed query because query itself does not have his own name. Let’s compare with named query:
query myVessels {
vessels(first: 3) {
nodes {
staticData {
mmsi
name
}
}
}
}Named queries are more generic just because they can have a variables and variables can be passed to arguments:
query myVessels($numOfVessels: Int!) {
vessels(first: $numOfVessels) {
nodes {
staticData {
mmsi
name
}
}
}
}To execute the query you need to provide query variables alongside with query as json:
{
"numOfVessels": 10
}On the network level named query with arguments are represented as extended version of POST request:
POST https://api.spire.com/graphql
{
"operationName": "myVessels"
"query": "
query myVessels($numOfVessels: Int!) {
...
}
",
"variables": {
"numOfVessels": 10
}
}The more realistically looking example of the query with variables:
query queryVesselsPositions(
$limit: Int
$after: String
$startTime: DateTime!
$endTime: DateTime!
) {
vessels(
first: $limit
after: $after
lastPositionUpdate: { startTime: $startTime, endTime: $endTime }
) {
pageInfo {
endCursor
hasNextPage
}
nodes {
id
staticData {
name
mmsi
imo
}
lastPositionUpdate {
timestamp
updateTimestamp
latitude
longitude
heading
speed
rot
accuracy
course
maneuver
navigationalStatus
collectionType
}
}
}
}Renaming fields
It’s possible to change the name of the field in GraphQL. You can rename any field, at any level of the query.
The syntax for renaming is always newName: fieldName for any field.
query queryVessels {
vessels(mmsi: [244234000]) {
nodes {
staticData {
imo
mmsi
call_sign: callsign
ship_type: shipType
}
}
}
}The response will look like:
{
"data": {
"vessels": {
"nodes": [
{
"staticData": {
"imo": 9361354,
"mmsi": 244234000,
"call_sign": null,
"ship_type": null
}
}
]
}
}
}You can change the name of the field in the query, but you can’t change structure of the query. For example, mmsi will always be child of staticData.
Multiple Root Fields
One query can contain multiple root fields. We need to use the renaming feature of GraphQL syntax to query multiple vessels fields. The two root queries tankers and cargo will be executed in parallel, but response will come when both of them are resolved.
{
tankers: vessels(shipType: [TANKER_CRUDE, TANKER_PRODUCT, TANKER_CHEMICALS]) {
nodes {
staticData {
mmsi
name
}
}
}
cargo: vessels(shipType: [CONTAINER, GENERAL_CARGO]) {
nodes {
staticData {
mmsi
name
}
}
}
}The response will look like:
{
"data": {
"tankers": { ... },
"cargo": { ... }
}
}Notes:
- Each root query is resolved in parallel, but the entire result will come when all root queries will be resolved.
- If you query multiple root queries, you might need to deal with multiple pagination cursors. Each sub query will have an independent pagination cursor.
- Each root query counted once for rate limiter.
Fragments
A fragment is a reusable piece of GraphQL query. For example, for some vessels you are interested in last position, but for another vessels you are interested in the current route:
query {
vesselsWithPosition: vessels(mmsi: [244234000, 413801932, 259605000]) {
nodes {
id
staticData {
imo
mmsi
callsign
shipType
}
lastPositionUpdate {
collectionType
latitude
longitude
}
}
}
vesselsWithVoyage: vessels(mmsi: [412338057, 338164033, 710127102]) {
nodes {
id
staticData {
imo
mmsi
callsign
shipType
}
currentVoyage {
destination
eta
}
}
}
}You can see that staticData part is duplicated across the queries and we can extract it to the fragment and reuse:
query {
vesselsWithPosition: vessels(mmsi: [244234000, 413801932, 259605000]) {
nodes {
id
staticData {
...vesselStaticData
}
lastPositionUpdate {
collectionType
latitude
longitude
}
}
}
vesselsWithVoyage: vessels(mmsi: [412338057, 338164033, 710127102]) {
nodes {
id
staticData {
...vesselStaticData
}
currentVoyage {
destination
eta
}
}
}
}
# NOTE: fragment declared outside of the query brackets query { ... }
# Declare fragment on type
fragment vesselStaticData on VesselStaticData {
imo
mmsi
callsign
shipType
}Notes:
A fragment must be used within the query, otherwise a GRAPHQL_VALIDATION_FAILED error will be returned.
You can have several fragments on one type and use them at the same time.
Unions
Usually when you query a field it has a single possible type. GraphQL unions are used to represent scenario scenarios when there are several possible return types for the same field.
For example, when you query predictedVesselRoute, depending on the origin argument, the route could start from a point or from a port. In the query only one of these branches will have a result depending how origin is specified:
If the origin is provided as unlocode then it will resolve to ... on Port branch.
If the origin is provided as coordinates then it will resolve to ... on GeoPoint branch.
{
predictedVesselRoute(
vessel: { mmsi: 205283000 }
origin: { unlocode: "TTPTS" }
destination: { unlocode: "COBAQ" }
) {
journey {
origin {
# if origin is geo point (NO)
... on GeoPoint {
latitude
longitude
}
# if origin is port (YES)
... on Port {
name
unlocode
centerPoint {
latitude
longitude
}
}
}
}
}
}Will result in:
{
"data": {
"predictedVesselRoute": {
"journey": {
"origin": {
"name": "Point Lisas Ports",
"unlocode": "TTPTS",
"centerPoint": {
"latitude": 10.400300025939941,
"longitude": -61.49700164794922
}
}
}
}
}
}Making API calls
Authentication
The Maritime 2.0 API uses Bearer tokens to authenticate requests. Attempting to make requests to the API without a valid API Key will result in the return of an error message.
In addition, to ensure transport layer security, all access or communication with the APIs must be made over HTTPS.
Not a Spire customer yet?
You’ll need a token to start using the API. Get in touch with our team to purchase an API plan or request a trial token.
https://api.spire.com/graphqlAll requests should contain following header:
Authorization: Bearer <token>
curl \
--request POST \
--url https://api.spire.com/graphql \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer " \
--data '{ "query": "{ vessels(first: 1) { nodes { id staticData { name mmsi imo } lastPositionUpdate { timestamp latitude longitude collectionType } } } } " }'
Supported types
Default scalar types
Boolean- The Boolean scalar type represents
trueorfalse. Float- The Float scalar type represents signed double-precision fractional values as specified by IEEE 754.
Integer- The Int scalar type represents non-fractional signed whole numeric values.
Int can represent values between-(2^31)and2^31 - 1. String- The String scalar type represents textual data, represented as UTF-8 character sequences.
The String type is most often used by GraphQL to represent free-form human-readable text. ID- The ID scalar type represents a unique identifier, often used to fetch an object or as the key for a cache.
The ID type is serialized in the same way as a String; however, defining it as an ID signifies that it is not intended to be human‐readable.
When expected as an input type, any string (such as"4") or integer (such as4) input value will be accepted as an ID.
Maritime 2.0 scalar types
IMO- Vessel’s IMO number
MMSI- Vessel’s MMSI number
DateTime- A date-time string at UTC, such as
2007-12-03T10:15:30Z, compliant with thedate-timeformat outlined in section 5.6 of the RFC 3339 profile of the ISO 8601 standard for representation of dates and times using the Gregorian calendar. GeoJsonPosition- Represents a pair of coordinates in a decimal format:
[number, number] WKT- Geometry in a Well-Known Text format.
UNLOCODE- UN/LOCODE as defined by the UNECE
The TimeDuration field
We defined the TimeDuration field to represent the time duration in various formats.
The type has 3 properties each representing a different format:
iso- Represents duration in ISO 8601 format; e.g.
PT24H5M30Srepresents 24 hours, 5 minutes, 30 seconds. seconds- Represents duration in seconds
text- represents duration in human-readable text, e.g.
1h1m45s
Writing queries
To access the data, you will need to execute a query against the Spire Maritime 2.0 service.
Each query is mapped to a specific object type, and each object type has certain fields that can be included or excluded in the query schema to get the desired results.
For more information about each object type, please refer to the Output section of the Fundamentals page.
To filter the results returned in the query (ie. getting information for a specified list of MMSI or limiting results to a confined area of interest), you will need to specify arguments in parentheses next to the query name.
The queries below are intended to be run in the Playground environment:
Return all vessels globally
Sample of a query that returns all vessels globally.
The sample below includes some, but not all available fields:
query {
vessels {
pageInfo {
hasNextPage
endCursor
}
totalCount {
relation
value
}
nodes {
id
updateTimestamp
staticData {
name
imo
mmsi
}
lastPositionUpdate {
latitude
longitude
navigationalStatus
timestamp
updateTimestamp
}
currentVoyage {
destination
draught
eta
timestamp
updateTimestamp
}
}
}
}Return partial fields for all vessels globally
In order to modify what fields are returned in the response, simply modify which fields you request in the request schema.
For example, if you would like to only get positional information about the vessels (no static information), you would use this sample query:
query {
vessels {
nodes {
id
lastPositionUpdate {
accuracy
collectionType
course
heading
latitude
longitude
maneuver
navigationalStatus
rot
speed
timestamp
updateTimestamp
}
}
}
}To further specify which data you would like returned in the response, you would add/delete the fields in the request schema.
It is important to note that for GraphQL queries you do not need to make multiple requests to access different resources.
For example, if you are only interested in the following fields:
idandupdateTimestampfields- the vessel
name,mmsi, andimofields of thestaticDatatype - the
collectionType,latitude,longitude, andtimestampof thelastPositionUpdatetype - all pagination-related fields from the
pageInfotype
… the query schema would look like this:
query {
vessels {
pageInfo {
hasNextPage
endCursor
}
totalCount {
relation
value
}
nodes {
id
updateTimestamp
staticData {
name
mmsi
imo
}
lastPositionUpdate {
collectionType
latitude
longitude
timestamp
}
}
}
}Pagination
There are two arguments in the query used for pagination:
firstInt- Identify how many elements per page you are requesting
afterString- Cursor value identifying position to continue pagination.
To query specific number of vessels provide a first argument to the query. The following example returns the first 10 vessels with the recent timestamp:
query {
vessels(first: 10) {
nodes {
staticData {
name
mmsi
imo
}
lastPositionUpdate {
timestamp
latitude
longitude
collectionType
}
}
}
}To enable pagination you need to provide a after argument to the query. The after is equal to the endCursor value from your most recent API request.
Thus, to determine the after value, first make your initial query and request the endCursor field:
query {
vessels(first: 10) {
# pagination information
pageInfo {
hasNextPage
endCursor
}
nodes {
staticData {
name
mmsi
imo
}
lastPositionUpdate {
timestamp
latitude
longitude
collectionType
}
}
}
}This should return results similar to:
{
"data": {
"vessels": {
"pageInfo": {
"hasNextPage": true,
"endCursor": "28a3e8d2-6404-4bd0-9d73-5446c70b78fe@99"
},
"nodes": [ ... ]
}
}
}Now that you have the endCursor value of your last API request, use this value as the after value in your next request.
query {
vessels(first: 10, after: "28a3e8d2-6404-4bd0-9d73-5446c70b78fe@99") {
pageInfo {
hasNextPage
endCursor
}
nodes {
staticData {
name
mmsi
imo
}
lastPositionUpdate {
timestamp
latitude
longitude
collectionType
}
}
}
}The hasNextPage value controls the pagination. If it’s false than next page is not available and endCursor: null.
Filtering
You can pass arguments to fields in order to filter the API results. What you can filter on is determined by the query schema.
For example, in the vessels query, the schema looks like this:
vessels(
after: String
areaOfInterest: AreaOfInterest
callsign: [String!]
first: Int = 100
flag: [String!]
imo: [IMO!]
lastPositionUpdate: TimeRange
mmsi: [MMSI!]
name: [String!]
shipType: [ShipType!]
lastTimestamp: TimeRange
): VesselConnection!In the schema above, all the keywords (ie. mmsi, imo, etc.) are the arguments you can pass to the vessels query within the parenthesis.
For more information about arguments check out GraphQL’s documentation.
Filter by a specified MMSI list
Use the MMSI filter in the sample of a query to return data for a given MMSI list.
You can see in the sample query that an argument is used to filter on the vessels field, as denoted by the parentheses () next to vessels before the response schema is described in the curly brackets {}:
query {
vessels(mmsi: [412219791, 338153238, 414403750]) {
nodes {
staticData {
aisClass
flag
name
callsign
mmsi
callsign
dimensions {
a
b
c
d
width
length
}
}
lastPositionUpdate {
latitude
longitude
}
currentVoyage {
destination
draught
eta
timestamp
updateTimestamp
}
}
}
}Filter by long lists of MMSI
Maritime 2.0 GraphQL allows queries up to 10Kb in size. This means that it is in theory possible to query up to 10,000 IMO or MMSI numbers.
If you want to query information for a specific fleet of vessels identified by IMO number or MMSI number then it is possible to query up to 10,000 at a time.
The vessels root query of Maritime 2.0 GraphQL will return up to 1,000 vessels per page of results, however using an advanced GraphQL technique to request multiple lists of vessels will potentially return more results in each combined result set.
The query below shows how to submit a query for 2,948 vessels filtered by imo. A similar query structure can be used to query any list of IMO or MMSI numbers that you need to construct.
query {
part1: vessels(
imo:[ 9926934,9928085,9789037,9928097,9941520,9940320,9778923,9918420,9918157,9929194,9918418,9938573,9938535,9925667,9931862,9937957,9903425,9889916,9938511,9926946,9938523,9789049,9884473,9789051,9927316,9937945,9931874,9943920,9903451,9945203,9941518,9928073,9938585,9934668,9903437,9937969,9888766,9889904,9941221,9924869,9945198,9894416,9903449,9918145,9936549,9941219,9928061,9931850,8766179,9820881,9914058,9933444,9939917,9929209,9555008,9934486,9934474,9925679,9915806,9831684,9739185,9757694,9915105,9915090,9901362,9937115,9932323,9918767,9862293,9936288,9436161,7830038,9687904,9870757,7368231,9746968,7229447,7320344,7400704,7382720,7302172,8029686,8613384,7900883,7823645,7718723,7929798,8013962,7913866,7353236,7926447,7238682,7924023,8027688,7921887,7232717,7909011,8016184,8029674,8108925,7331587,7909839,9402380,7830026,7122687,8920000,7022502,9112143,8022212,8511249,7301714,8014057,9074858,7718694,7230604,7405015,7915993,7603332,7335686,7010664,7107699,7931090,8323525,7701562,8004313,9016698,8011043,7422374,7921875,7623631,8005692,8029698,7930448,9914228,8029662,8208426,7326570,7611743,7434482,8319043,7401198,8317382,7821556,7514505,7109403,7025700,8919908,8515879,8516897,7353509,7238096,7810569,7033329,7116119,7718412,8004014,8504222,7022148,9564657,7349613,7359955,8121458,8801046,7723704,8111855,7921899,8419805,9007570,8111843,7405041,8506426,8903131,7924035,8024040,9020479,9020481,7904205,9596856,8811754,7928201,7405003,8217910,8024038,7343267,8005393,7522382,7405039,8812825,8821682,7905522,7928641,7640201,7924047,7224100,9176694,9886794,9000481,7904190,7708687,8111867,8813104,8013625,7700855,8217908,7383499,7405053,8002664,8012281,9170597,7640196,7405027,8027690,7708675,8506438,7640184,8108731,8303654,8821670,8821694,8005408,8903129,8804725,8311297,8715883,8908569,8810188,8608456,7113674,8715895,9129718,7211921,8511964,8013223,7531345,8123688,8100765,7350973,8705711,8705723,8013259,8013247,7373365,7411088,7411076,8030192,7379773,8955378,7044158,7501376,8105052,7373353,7391874,8206612,7402269,7415204,7415216,7352672,7226902,8417261,9010797,7909346,8501531,8501543,8712570,8409630,8902747,8511031,8919752,8912194,8026012,7106944,8325315,7211361,8325327,7126164,7508520,7348968,7040982,7311604,7348970,7424528,9005479,8203232,9039743,9008471,9008469,7315260,7424516,8002951,9112155,9005481,9201906,7600275,7707724,8012865,7328097,8002133,8402345,8222214,8914300,9007087,7509184,8324634,8716514,9007099,7419107,7611793,7419092,7102209,7026716,8016196,8515453,8515465,9034511,7604867,9034509,7522112,7211359,8008383,8400165,7601047,7020097,7038197,7408861,8400177,7931105,8411700,7514361,7811331,7357452,7533707,7817268,9771470,7319711,7414145,8814756,8003010,7120756,8128975,7384481,7712925,7638337,7411557,9002491,8010738,7379761,7327976,8114716,7723857,8128963,7321544,7359917,8406054,8912182,7405625,8116570,7401186,7112058,8807650,7347665,9021667,7383516,7417642,8016809,7411064,8403416,9009023,7414028,7214454,7235965,7411571,8017061,7354840,7384493,8116582,8123626,8814768,7223077,7402506,7907453,7420077,7016852,8001763,8302985,8131104,7383528,8406767,7411052,7420297,7420302,7403067,8102505,8405971,8110552,7422221,8323173,7401174,7901540,7218539,7379711,7411533,7413244,9005508,7034971,7223065,7411545,7359864,7400687,8414178,8716215,8123638,7723869,7383475,8803381,7414133,8008474,8107141,7121310,8000989,7414121,8416334,7721081,7405326,9900485,9765251,7326568,8910811,8029442,7354151,7530638,7626695,7501522,8017932,7818298,8029753,9313838,8014112,9867138,7904229,7204904,7927130,9866017,7916181,9881184,8911188,9901269,9539028,9699402,9887554,7114692,7629635,8028943,7016008,8413007,8001957,8710170,8018077,8604486,7916258,7909138,9889069,7714545,9005728,8016835,7352282,8520587,8518663,7330741,8805119,8795285,7391197,7368841,8210209,7428433,8013950,9030840,7391202,7391214,7428445,7359670,7121633,7347732,7217896,7428471,7235939,7428469,7347794,7347768,8700577,8922357,9017252,8818817,9228887,8903208,8818805,9228875,8026373,9003067,9013696,8705955,7369144,9003043,9003079,9016064,8012114,7325394,7304326,8532736,9625308,8124515,7401203,7359876,7403079,8206624,7363243,7383504,7727346,8109395,9005015,9009190,9128661,7354163,8902797,8717922,9032264,8817992,9014779,8913215,7402257,8818001,8718720,9006693,9016739,8009387,8906810,9014781,8718469,8219932,8904056,8806216,8129814,7126712,7633117,9015759,8024337,8110394,8619405,8910720,9165011,8125832,8702941,8110203,8014409,7411961,7360124,7702401,7035494,7708948,7229459,7359785,8014473,7039074,8828343,9282429,7328243,7390179,7400675,7390155,7400663,7619587,7390208,7619575,7390167,7413232,7390143,7048453,7038692,8972132,9829590,9943499,9540089,9943504,9918353,9908360,9889590,9317200,8515063,9132648,9152337,9146845,9597458,7823762,7903811,8709004,9056521,9239680,7709473,8322002,9003990,9239965,9523586,9693305,7916569,9009827,9157583,9537305,9632674,9715957,7626918,7904176,8915079,8904989,9136759,9196333,9889588,9165047,9380984,9372779,9540754,9781798,9233909,8921511,9691333,7620756,8005630,9128867,9277876,9005168,9114646,9380946,9442079,9874882,8013376,9191242,9365051,9469998,9606572,9682198,9749283,9203239,9197624,7706392,9031753,9066502,9135559,9266217,9473614,9523732,9673745,9798624,8820688,9309552,9523744,8513857,8822284,9016284,9528550,7405431,7913854,9201126,9888780,7921643,7927489,8820171,8921535,8609101,8801709,9088627,7429566,9715969,9035668,9268021,9448853,9852250,9143128,9300702,7930187,9046887,9157557,9873723,7124166,8415392,8510063,9523330,8319196,9202132,9218129,9512874,9644768,7921679,9058830,9134361,8021880,9046875,9402988,8021878,8204561,8609096,9119256,9146235,9183879,9368170,7908677,9176280,9296688,9317286,9343704,8911164,9163116,9893541,9926570,9360295,8313154,9151448,9682227,7810674,7810727,7913878,9132882,9228631,9622722,9805398,8217128,8822258,7921411,8114259,8613372,9109574,9288629,8416619,9132636,9189976,9380996,7376173,8014899,9154177,8022028,8025410,9128881,9333096,9368089,9512836,9682215,9882712,9009994,9185580,9597460,9890343,8608987,9166936,9392200,7916272,8114247,9005962,9058555,9136747,9197210,9195274,9890367,9606687,9015319,9911161,9912206,9898022,9854416,9907691,8955366,9183805,9482005,9854428,9572551,9466403,9618408,9898010,9799305,9260603,9469235,9554729,9433884,9675200,9110092,9217967,9512886,8920127,9168283,7429449,8514277,8605143,9047283,9392042,9909390,7909152,9355305,8921884,9189017,9912579,9203241,9110066,9142277,7629568,9364174,7909140,9046801,9219953,9314416,9571222,8005642,8616685,8002195,7930230,8916322,9054717,9216793,9691321,7823774,9003641,7616559,9009803,9072757,9737541,9021411,9167394,7810739,8915316,8312502,7334498,7535535,7908665,9363522,7700752,9152313,9810161,8816261,9810147,7714973,9217450,9256896,7016228,9088677,9207144,9078660,9622095,7820760,9020833,9837585,9005716,9113991,7322380,9711262,8223543,8609216,9597965,7923067,8717726,9496197,8514186,9634878,9392030,9601871,9309564,9063512,9020857,7706299,8202587,8910330,9364162,9564853,9355290,7914030,9145891,9226607,9152349,9184146,7927427,9447378,9826861,9379234,9810159,8401705,9012159,9124275,9388429,9020704,9743863,7000059,9122253,9771937,8103901,9330123,9805958,8704248,9805960,9058660,7009172,9749477,7428457,8125868,9627930,9468047,9050474,7330179,8005666,8514198,8110215,9111503,8605674,8801682,8610473,9894076,8416633,7818925,8005678,8106422,7044237,8710156,9565833,7912898,9627942,9894040,9820415,9845881,9515814,7331290,8608896,9606481,9627734,9672480,8122995,8608638,7035119,7623708,9491446,7916064,9894064,9378266,9370666,9370654,9089968,8215819,9003275,8521488,8700541,9003287,9654878,9630004,9654880,9810367,9810379,9630028,9743916,9743928,9690157,7390181,9064073,9064085,7382732,7361934,7382744,7361922,8008280,9031973,9031985,9404584,8910902,7411569,9193733,9306548,9290270,8910897,7420089,9195494,9257395,9108099,9193721,8917807,9002908,9177545,9402562,9378163,9402574,9177583,9177569,9358682,9147394,7230666,9155626,9173070,9177571,9177557,9155341,9888194,7624805,7521273,9352860,9768394,9744025,9888481,9878876,9886732,9918781]
){
pageInfo{
endCursor
hasNextPage
}
totalCount{
relation
value
}
nodes{
staticData{ name flag aisClass callsign timestamp mmsi imo shipType shipSubType updateTimestamp }
currentVoyage{ eta draught timestamp destination updateTimestamp }
lastPositionUpdate{ timestamp latitude longitude collectionType heading speed course updateTimestamp }
}
}
part2: vessels(
imo:[9434266,9627485,9693161,9861031,9870159,9943853,9892298,9917543,9333620,9412880,9413327,9682605,9819650,9414632,9661869,9759240,9810549,9877133,9629598,9636735,9682588,9693173,9349019,9892456,9369899,9401295,9600530,9723801,9915894,9892121,9355379,9627954,9869942,9904699,9306495,9878723,9874466,9878711,9640645,9738569,9857365,9872949,9874040,9904170,9624914,9633173,9610767,9810020,9834325,9872999,9879698,9902756,9922976,9917567,9333606,9361990,9501186,9658238,9690169,9791212,9383900,9658240,9707510,9834313,9884021,9390185,9680188,9779238,9857377,9606948,9765079,9862906,9918793,9682590,9875800,9368302,9626027,9626285,9636711,9654701,9680190,9926910,9496305,9626273,9892133,9919890,9896440,9269207,9640023,9862475,9918834,9516129,9490961,9617698,9768368,9862918,9902902,9922988,9737187,9709491,9834296,9874480,9869306,9904194,9320075,9636723,9627497,9690145,9744013,9845776,9872901,9903920,9917579,9761243,9760770,9636785,9654696,9640437,9633161,9637492,9864746,9862920,9902926,9904687,9904675,9331660,9864916,9877145,9943841,9904704,9655042,9750696,9750725,9863182,9909613,9360922,9491812,9650054,9750701,9758832,9895238,9905980,9333632,9634086,9629586,9636797,9634098,9650042,9692014,9690171,9761267,9736092,9834301,9905978,9929106,9918846,9355604,9600528,9637325,9864667,9864784,9918808,9692002,9758844,9853137,9886744,9926908,9774628,9748904,9361639,9369904,9610779,9768382,9855812,9864796,9904182,9339260,9732371,9759252,9336737,9331672,9816763,9896452,9496317,9750672,9862346,9862891,9876737,9878888,9904209,9918822,9904546,9926714,9645970,9637507,9624938,9638903,9696266,9638915,9682552,9748899,9750660,9876660,9885996,9627966,9659725,9880192,9862463,9915909,9490959,9682576,9752565,9917555,9918860,9333618,9425277,9624926,9750737,9791200,9368314,9655444,9810551,9893606,9627502,9750713,9333591,9477593,9626039,9636747,9633422,9709489,9750658,9874454,9606950,9760782,9849887,9852975,9851787,9884174,9918779,9696735,9870525,9864928,9872987,9902938,9918858,9926922,9707508,9750749,9769855,9845764,9904651,9918810,9768526,9349007,9377547,9342487,9520376,9475208,9633434,9845788,9915911,9336749,9635315,9655456,9768370,9774135,9693719,9760768,9862487,9869265,9902914,9885855,9762039,9772852,9869241,9883819,9849631,9869253,9809552,9849629,9772826,9847956,9822451,9823883,9655808,9837066,9780354,9854935,9778313,9820013,9724946,9785500,9859820,9684495,9868974,9880764,9870472,9769128,9850680,9750024,9886756,9909285,9830898,9819882,9888182,9870628,9830903,9868962,9886768,9859636,9715701,8915421,9715713,7901277,8915419,9653678,9674907,9633991,9629536,9629524,9762962,9390680,9385673,9624940,9480409,9685504,9402586,9008500,9070072,9417361,9744960,9158240,9378151,9771511,9744958,9512848,9480382,9566306,9685451,9040118,9129392,9566289,9685437,9685449,9013701,9129380,9566291,9402598,9358670,9685425,9053816,9771523,9654971,8705943,9685499,9941568,9830757,9830745,9523823,9564073,9642033,9584528,9688178,9629421,9233674,9584516,9486946,7525736,9629354,9642150,9630353,9610107,9635092,7904164,8608901,9761607,9532018,9651735,9629433,9635107,9710804,9578878,9655949,9519690,9584530,9640487,8304244,9615016,9613408,9817743,9655937,9819430,9569580,8319134,9634074,9642124,9651747,9847152,9351866,9537123,9537111,9413030,9351854,9877341,9779226,9874492,9864837,9809540,9770531,9560467,9792515,7611781,7617814,7649855,7808994,8905830,9130494,9337963,9742819,9360879,9825439,9904211,9431135,9613147,9798167,9360843,9397339,9694751,9914632,9762273,9431111,9431214,9687019,9694749,9753026,9750256,9932581,9758064,9781918,9753014,9681699,9850678,9360881,9881201,9862308,9859739,9909388,9468437,9732369,9613161,9705653,9785158,9388821,9443413,9941245,9337717,9681687,9766566,9337987,9397298,9761839,9879674,9431123,9672832,9709025,9922782,9433717,9851646,9873852,9896921,9901350,9337729,9397341,9397353,9443683,9761853,9761803,9851634,9859753,9880477,9924857,9918054,9932608,9907926,9372743,9770945,9854363,9887217,9850666,9914644,9337755,9672818,9854612,9388819,9770933,9929871,9337975,9721724,9672844,9761815,9918004,9337705,9360805,9360829,9761827,9766530,9360867,9904091,9397303,9701229,9845013,9892717,9918030,9613135,9721401,9770921,9825427,9918016,9372731,9397315,9687021,9698123,9767962,9896933,9649328,9705641,9859741,9337951,9337731,9443401,9929132,9360831,9672820,9831220,9922770,9360817,9337743,9418365,9873840,9907782,9750244,9766554,9781920,9854765,9360855,9701217,9892822,9750220,9854624,9431147,9761841,9388833,9750232,9766578,9468449,9360790,9613159,9767950,9874820,9338266,9792606,9883742,9941233,9922768,9360908,9918028,9721736,9909417,9926752,9709037,9742807,9766889,9844863,9762261,9766580,9825568,9397286,9892834,9360893,9766542,9771913,9918042,9397327,9758076,9880465,9854375,9771080,9687485,9686376,9780732,9735036,9726114,9232503,9409302,9659103,9689926,9733325,9791224,9835185,9852133,9901984,9901996,9938054,9451991,9721138,9732527,9749788,9800491,9933468,9537032,9732515,9722223,9765457,9919175,9935480,9307750,9346122,9448487,9631682,9802293,9914620,8917845,9445954,9643348,9726061,9735062,9719305,9903073,9645358,9710385,9739977,9763813,9687502,9743722,9765550,9780005,9409168,9689914,9682447,9721140,9735282,9797876,9795919,9372420,9405875,9590668,9734680,9725500,9847425,9810044,9409156,9536363,9701786,9703007,9852145,9656888,9706516,9722792,9739989,9726073,9776341,9789166,9810032,9876490,9919187,9937062,9350422,9666675,9685217,9659139,9667540,9699995,9732503,9787352,9792747,9923097,9415686,9447809,9479929,9649146,9735787,9867102,9906269,9307762,9405083,9706487,9733337,9734513,9719410,9735660,9774197,9897547,9350288,9703019,9752711,9897092,9393682,9388687,9415662,9701798,9744843,9789726,9879703,9916812,9364382,9350599,9352963,9347516,9686388,9738234,9741827,9719290,9849617,9849277,9908839,9447794,9534810,9706499,9790220,9840867,9933781,9346134,9398307,9714393,9702015,9789324,9887451,9935507,9387762,9531478,9739953,9722807,9840879,9847944,9412086,9531519,9590670,9734678,9674842,9687514,9725495,9794288,9903085,9540091,9916824,9933767,9377793,9415703,9537044,9659115,9678525,9730139,9726085,9719408,9732539,9780641,9940605,9630755,9659127,9804253,9779991,9900851,9933509,9369760,9407122,9731042,9855941,9937074,9377078,9415698,9625152,9702039,9689548,9793246,9835173,9839739,9534614,9611955,9670004,9702041,9710397,9744128,9800099,9719276,9543081,9543079,9892951,9405887,9719501,9734525,9773234,9839727,9916836,9386304,9471018,9735658,9789154,9471032,9847437,9906922,9897559,9292113,9354624,9531507,9689536,9694622,9735048,9739965,9743734,9759185,9900849,9412062,9354935,9666974,9903762,9923085,9351919,9454010,9793260,9789312,9790232,9933511,9307748,9353242,9372432,9369461,9406269,9738246,9793258,9810056,9853864,9832793,9621584,9694634,9703837,9902172,9394208,9699517,9711846,9765562,9778478,9796585,9895771,9935492,9359454,9332066,9350290,9470088,9536375,9699505,9723681,9754824,9722780,9797864,9875408,9893656,9902809,9938066,9670016,9702027,9762118,9744831,9778480,9795672,9850367,9666663,9706504,9386299,9604392,9719496,9674854,9793234,9859882,9902794,9364394,9415648,9471123,9656747,9693549,9714381,9734692,9788992,9789714,9800506,9895305,9933779,9307736,9292759,9336658,9370537,9667564,9763045,9763033,9832808,9903140,9336660,9448504,9531466,9608300,9729269,9687497,9940447,9852949,9849289,9902512,9350604,9359466,9359478,9377224,9702003,9726126,9852951,9933523,9930296,9229233,9711834,9752723,9787340,9364966,9726102,9748227,9795543,9748215,9794135,9448499,9735050,9719288,9895317,9897107,9902782,9902160,9411733,9713105,9861811,9820843,9861809,9792591,9864318,9918171,9918183,9864966,9799379,9752307,9752606,9864306,9752292,9864954,9901403,9752278,9864978,9752280,9901398,9752618,7382691,9525194,9577991,9796169,9713612,9743241,9846328,9867281,9523794,9624809,9658367,9715921,9699256,9719513,9743253,9733569,9707182,9774898,9392250,9519676,9713648,9448865,9514303,9578012,9789532,9664938,9658355,9746774,9837793,9474553,9861201,9596234,9519688,9715945,9364198,9733533,9341902,9359557,9758818,9798636,9907794,9525170,9578024,9733545,9851610,9580182]
){
pageInfo{
endCursor
hasNextPage
}
totalCount{
relation
value
}
nodes{
staticData{ name flag aisClass callsign timestamp mmsi imo shipType shipSubType updateTimestamp }
currentVoyage{ eta draught timestamp destination updateTimestamp }
lastPositionUpdate{ timestamp latitude longitude collectionType heading speed course updateTimestamp }
}
}
part3: vessels(
imo:[9711482,9926283,9525211,9713545,9713624,9796171,9514298,9507740,9346407,9507726,9943229,9341897,9442184,9519535,9649768,9710309,9687667,9719525,9596868,9892808,9578036,9698367,9715933,9710323,9710335,9733571,9196450,9474541,9523809,9519523,9641041,9527013,9578048,9707194,9521588,9711470,9733557,9578000,9699244,9715555,9596820,9883558,9926582,9474539,9525209,9507752,9717412,9596832,9806720,9894088,9523811,9507764,9859698,9559640,9525182,9520132,9507738,9726827,9359569,9525223,9892793,9333137,9559652,9726815,9733624,9851622,9690121,9697507,9710311,9837808,9089982,9392236,9515981,9747065,9798947,9893383,9559731,9652753,9891854,9089994,9558945,9448877,9612844,9713557,9748978,9515266,9364186,9698355,9691345,9826407,9232321,9480370,9572563,9806732,9172131,9652741,9746786,9596844,9596870,9875719,9664926,9739549,9649770,9655509,9675078,9704518,9712565,9506162,9856476,9458169,9704520,9734850,9407328,9522257,9368792,9407330,9522269,9618848,9618850,9506186,9711511,9734848,9624005,9745512,9746671,9800178,9788980,9675066,9368780,9390953,9744790,9374569,9543043,9798179,9511650,9615092,9662019,9342396,9346914,9346940,9353979,9682265,9744946,9853577,9922225,9404792,9623984,9553660,9864291,9671216,9761164,9374911,9662021,9755658,9833199,9342384,9441685,9368194,9342425,9366940,9553634,9726322,9799381,9540003,9318618,9404807,9796705,9682253,9676228,9745536,9320855,9425241,9711494,9742326,9922213,9346926,9458171,9482574,9746683,9034729,9373735,9704506,9694373,9834715,9522271,9409314,9404780,9545211,9675080,9744910,9800166,9834727,9542984,9712553,9877470,9342401,9368778,9373591,9337793,9506150,9759264,9714630,9935478,9458157,9796339,9034717,9704532,9383338,9390965,9694385,9403786,9552719,9034705,9346902,9404819,9506198,9545209,9661807,9711535,9714654,9827205,9425253,9551777,9711523,9318620,9356919,9344203,9694397,9586679,9678989,9671228,9744934,9745524,9356921,9482586,9661558,9788966,9403774,9744922,9403762,9346938,9371660,9827217,9655511,9677612,9711509,9342413,9809045,9788978,9349928,9623996,9742302,9208148,9347736,9374557,9761176,9344198,9553646,9734836,9714642,9744776,9410624,9506174,9553622,9755646,9618862,9704491,9742314,7534579,7037076,9008512,9250713,9326689,9330745,9324435,9341299,9482304,9255854,9303560,9271248,9266994,9320386,9275335,9325702,9319404,9293844,9038440,9030838,9256793,9275347,9308431,9311579,9321744,9334284,9300817,9326603,9035864,9157739,9256597,9311567,9373008,9247364,9321756,9186584,9666986,9238040,9317315,9338797,9325893,9060534,9293832,9311581,9256767,9180243,9253703,9321653,9308481,9246578,9583677,9236420,9325685,9321665,9305116,9269960,9331048,9372963,9274226,9329679,9369473,9405588,9329291,9375721,9307205,9749609,9238038,9256200,9323687,9259276,9277620,9315393,9030814,9157624,9230050,9246621,9403669,9483877,9540716,9030802,9247194,9307190,9321768,9350927,9302499,9305128,9403671,9243148,9236418,9321770,9006681,9230048,9267003,9482299,9269180,9349942,9250191,9284192,9317999,9475600,9038452,9267015,9373010,9341689,9180231,9250725,9157636,9236432,9256602,9308479,9035852,9245720,9275359,9307188,9315692,9253715,9230062,9266982,9030826,9403645,9691137,9253105,9276389,9325697,9403657,9320374,9321732,9355264,9294264,7373327,9322255,9361445,9638525,9381134,9389643,9444649,9361079,9239616,9252539,7423914,9187837,9043457,9034523,9177466,8026385,8899720,9014951,9853383,9124005,7008685,9572587,7376197,9175884,8002157,8419441,9017135,8605090,8712831,8118346,9119115,8626123,7231816,9494981,9824590,9298040,9269374,9261578,9261566,9925461,9318321,9052331,9284025,9315680,9354612,9889552,9329722,9892406,9238284,9379399,9377236,9031519,8912546,9237747,9889576,8519966,9247819,9277943,9293430,9347504,9240421,8818207,9412074,9332042,9332030,9356892,8216007,9223540,9295581,9892391,9379404,8912558,9133836,9253818,9249049,9102198,9208239,9264908,9308493,9134165,9131539,9242209,8818843,9014420,9292773,9113379,9176369,9332078,9889564,9247807,9284013,9320738,9274563,9292101,9320752,9377781,8902993,9133824,9377248,9292761,9385685,9387750,9006679,9292216,9208227,9232515,9102203,9284831,9240419,9014432,9253820,9282106,9000883,9247209,9369772,9324746,9275426,9320764,9403877,9324734,9343118,9012886,9317987,9176357,9329710,9326598,9320740,9179270,9375460,9128685,9139945,9172129,9892779,9132820,9423126,9152351,9137595,9251183,9161065,9116230,9143130,9148609,9191785,9189859,9245081,9151149,9161077,9882889,9891127,9235842,9882891,9108843,9264192,9146572,9229142,9228253,9194658,9133707,9119725,9267962,9143142,9142318,9194646,9267974,9250505,9250517,9902067,9175846,9194672,9260366,9109885,9291224,9134359,9263966,9220421,9142966,9140126,9251171,9249685,9200469,9254264,9136486,8812837,9116228,9128879,9238131,9251121,9143154,9135781,9354222,9267950,9194660,8813087,9256535,9045807,9183568,9131096,9174359,9269269,9183570,9173068,9250684,8908557,9220794,9131101,9034690,9202039,9178678,9103398,9185346,9212462,9197727,8813099,8813116,9103403,9133109,9143506,8813063,9207039,9227261,9173056,9220809,9157478,9212577,9240158,8813075,9133094,9181900,9268394,9174361,9262948,8850918,9378292,9378280,9783124,9378307,9378278,9625140,9135793,9268679,9268681,9268693,9135779,9176125,8810700,9050187,9601742,9274379,9560168,9371672,9251781,9601754,9005493,8800298,9130456,9133549,9404625,9204922,9251779,8817693,9160475,9401570,9130468,9350898,8922292,9269271,9008483,8012853,8411243,9371684,9160487,9350886,9040170,9560170,9015010,9040883,9006150,9215141,9374882,9601730,8303240,9177959,7710678,7423897,7423885,9240122,9240146,9240134,9014963,9254953,9254941,9264910,9324332,9247962,9155078,9262235,9621077,9074640,9176008,9229647,9262211,9666560,9714288,9018555,9155145,9253222,8913150,9132791,9187356,9155157,9210816,9261205,9331658,9265500,9315719,9666998,8913174,9285952,9912880,9351971,9085651,9376294,9338955,9645748,9332054,9796793,9061928,9743875,9074626,9334076,9210828,9287948,9343106,9038816,9132741,9020766,9086746,9241267,9200316,9236614,9085625,9248502,9262209,9322803,8701791,9161510,9298399,9645736,9696149,9714276,9698111,8608872,8706155,8608884,9796781,9074638,9132818,9236626,9245031,9307176,9075333,9322815,9666558,9262223,9323675,9338929,9714290,9714305,9085637,9324277,9770440,9183269,9211872,9324344,9213416,9134323,9216303,9176010,9179581,9756389,9770438,8608705,9045132,9085613,9216298,9315707,9001784,9085649,9074652,9331634,9372999,9001772,9016492,9331646,9086734,9275074,9522415,9607758,8902371,9005053,9738545,9127033,9255701,9321225,9041655,9139696,9114581,9134294,9132789,9225342,9238272,9423322,9007386,9397080,9415650,9249336,9349784,9008108,9014456,9870513,9206384,9046784,9166766,9395501,9003859,9115303,9005065,9607069,9322657,9194969,9317298,9629873,9723679,9206396,9088536,9255713,9142150,8818219,9172636,9265548,9177806,9172739,9043677,9253284,9256614,9436159,8717934,9020455,9710294,9857016,8814225,9015149,9900174,9526980,9377951,9202821,9368924,9368936,9005182,9241176,9244415,9392858,9615341,9015137,9698290,9113927,9643972,9392860,9655016,9883560,9125994,9020132,9038763,9113939,9172753,9392884,9353981,9129691,9167409,9235270,9238959,9156797,9448841,9507582,9615353,9293600,9355123,9643960,9125401,9141962,9186948,9371189,9140592,9142136,9552721,8908246,9128673,9766619,9347475,9140607,9256729,8811766,9140633,9249697,9371177,9434541,9655004,8822143,9109304,9237890,9527001,9005106,9113941,9227118,9236901,9424754,9355135,9643984,9185827,9269312,9244403,9371165,9526992,9643996,9109603,9353993,9507594,9125413,9392872,9371191,9135561,9238129,9691319,9883572,9167411,9134971,9140449,9857004,9130391,9371153,9697492,9005118,9109316,9124744,9699608,9047116,9698288,9326201,9595539,9205574,9321885]
){
pageInfo{
endCursor
hasNextPage
}
totalCount{
relation
value
}
nodes{
staticData{ name flag aisClass callsign timestamp mmsi imo shipType shipSubType updateTimestamp }
currentVoyage{ eta draught timestamp destination updateTimestamp }
lastPositionUpdate{ timestamp latitude longitude collectionType heading speed course updateTimestamp }
}
}
}If you wanted to query a list of vessels by MMSI instead then you would simply replace the imo list with an mmsi list and the corresponding query filter.
Filter by AOI
Use the areaOfInterest argument to filter the data using an AOI.
This could either be a GeoJSON or WKT formatted AOI (there is no need to include both geoJson AND WKT in the same request).
query {
vessels(
areaOfInterest: {
polygon: {
type: "Polygon"
coordinates: [
[
[-122.662353515625, 37.54239958054064]
[-122.13226318359375, 37.54239958054064]
[-122.13226318359375, 37.8813571797486]
[-122.662353515625, 37.8813571797486]
[-122.662353515625, 37.54239958054064]
]
]
}
}
) {
nodes {
staticData {
name
mmsi
}
lastPositionUpdate {
heading
latitude
longitude
}
}
}
}Filter by a specified callsign
Returns data for the vessel with the callsign of "BOAG9".
query {
vessels(callsign: "BOAG9") {
nodes {
staticData {
name
mmsi
imo
}
lastPositionUpdate {
timestamp
latitude
longitude
collectionType
}
}
}
}Filter by a specified vessel flag
Returns data for vessels with the flag of "US".
query {
vessels(flag: "US") {
nodes {
staticData {
name
mmsi
imo
}
lastPositionUpdate {
timestamp
latitude
longitude
collectionType
}
}
}
}Filter by a specified IMO
Returns data for the vessel with the imo of 9538907.
query {
vessels(imo: [9538907]) {
nodes {
staticData {
name
mmsi
imo
}
lastPositionUpdate {
timestamp
latitude
longitude
collectionType
}
}
}
}Filter by specified lastPositionUpdate
Returns data for vessels with last position updated between timestamps "2021-08-02T00:31:42.780Z" and "2021-08-04T00:31:42.780Z".
query {
vessels(
lastPositionUpdate: {
startTime: "2021-08-02T00:31:42.780Z"
endTime: "2021-08-04T00:31:42.780Z"
}
) {
nodes {
staticData {
name
mmsi
imo
}
lastPositionUpdate {
timestamp
latitude
longitude
collectionType
}
}
}
}Filter by specified lastUpdate
The lastUpdate filter, added in August 2022 to Maritime 2.0, allows vessels to be queried for any update that was made within the filter time window.
lastUpdate is different from lastPositionUpdate because it will also return vessels that have non positional updates in the period requested. This will allow for vessels with static data or voyage updates to be returned as well as those with positional updates.
Here is an example, comparing its use with that of the lastPositionUpdate filter:
query {
vessels(
lastPositionUpdate:{
startTime:"2022-07-15T09:00:00.00Z"
}
shipType:[TANKER_CRUDE]
){
totalCount{
relation
value
}
}
}In the example above, requesting vessels with position updates returns an estimated 2208 vessels:
{
"data": {
"vessels": {
"totalCount": {
"relation": "LOWER_OR_EQUAL",
"value": 2208
}
}
}
}Let’s compare with the usage of the lastUpdate filter:
query {
vessels(
lastUpdate:{
startTime:"2022-07-15T09:00:00.00Z"
}
shipType:[TANKER_CRUDE]
){
totalCount{
relation
value
}
}
}In the example above, requesting vessels with any update returns a higher estimated number of 2667 vessels:
{
"data": {
"vessels": {
"totalCount": {
"relation": "LOWER_OR_EQUAL",
"value": 2667
}
}
}
}Filter by specified name
Returns data for vessels with a vessel name of "EAGLE".
query {
vessels(name: "EAGLE") {
nodes {
staticData {
name
mmsi
imo
}
lastPositionUpdate {
timestamp
latitude
longitude
collectionType
}
}
}
}Filter by specified shipType
Returns data for all General Cargo and Container vessels.
query {
vessels(shipType: [GENERAL_CARGO, CONTAINER]) {
nodes {
staticData {
name
mmsi
imo
}
lastPositionUpdate {
timestamp
latitude
longitude
collectionType
}
}
}
}Filter by fleet
In legacy Vessels API it was possible to filter only on the general AIS ship_type values like Tanker or Cargo.
Maritime 2.0 graphQL filters vessels on specific commercial ship types instead – a full list is available under the vesselStaticData section. If you want to receive the equivalent filter results as were provided in Vessels API then the filters in Maritime 2.0 for Cargo and Tanker are shown below:
Cargo Vessels
shipType:[CAR_CARRIER,COMBINATION_CARRIER,CONTAINER,DRY_BULK,GENERAL_CARGO,LIVESTOCK,REEFER,ROLL_ON_ROLL_OFF]Tanker Vessels
shipType:[GAS_CARRIER,GENERAL_TANKER,LNG_CARRIER,TANKER_CHEMICALS,TANKER_CRUDE,TANKER_PRODUCT]Merchant Fleet
shipType:[CAR_CARRIER,COMBINATION_CARRIER,CONTAINER,DRY_BULK,GENERAL_CARGO,LIVESTOCK,REEFER,ROLL_ON_ROLL_OFF,VEHICLE_PASSENGER,PASSENGER,GAS_CARRIER,GENERAL_TANKER,LNG_CARRIER,TANKER_CHEMICALS,TANKER_CRUDE,TANKER_PRODUCT]Filter by specified lastTimestamp
Unlike the filter lastPositionUpdate which filters for vessels by the time when a position update was received, the filter lastTimestamp filters vessels on the message timestamp of any update from AIS static or position messages.
If the lastTimestamp filter is not specified in a query then it will be set by default to filter out vessels with no AIS message in the last 30 days.
Returns data for all vessels updated after "2022-01-01T00:00:00.00Z":
query {
vessels(
lastTimestamp: {
startTime:"2022-01-01T00:00:00.00Z"
}
) {
nodes {
staticData {
name
mmsi
imo
}
lastPositionUpdate {
timestamp
latitude
longitude
collectionType
}
}
}
}Error handling
Handling errors in GraphQL is different compare to other API styles in a several aspects:
- GraphQL response is always
HTTP 200 OK - GraphQL errors is just data, it’s not linked to HTTP error statuses and does not inherit HTTP semantics at all
- It’s possible to return query data as well as an array of errors. In this case query data will contain partial results
The successful GraphQL response contains just a data field with result of the query:
{
"data": { ... },
}When an error occurs, the GraphQL response will contain an errors array. In this case data might be null or might be an object, but with a complete or partial results, depending on the nature of the error:
{
"data": { ... } | null,
"errors": [...],
}For example, the following query contains an invalid cursor value:
{
vessels(first: 3, after: "bla-bla") {
nodes {
id
staticData {
mmsi
callsign
}
}
}
}…which yields the the following response:
{
"data": null,
"errors": [
{
"message": "Invalid cursor provided for the after parameter: a",
"locations": [{ "line": 2, "column": 3 }],
"path": ["vessels"],
"extensions": {
"code": "BAD_USER_INPUT"
}
}
],
"extensions": {
"requestId": "7246b710-145d-4528-9c74-972287dc713a"
}
}Error format
We use a standard error format for errors, which means that all errors have the same structure.
Let’s explore the error from the previous example:
{
"message": "Invalid cursor provided for the after parameter: a",
"locations": [{ "line": 2, "column": 3 }],
"path": ["vessels"],
"extensions": {
"code": "BAD_USER_INPUT"
}
}…where:
messageis thestringwhich describes the errorlocationsshows where in the query string document this happenedpathis an array of paths leading to the field in error from the root of the queryextensionsis an object with any additional metadata about an error such as an error code.
Note that:
- The object
errors.extensions(described above) is not to be confused with the top-level objectextensionsthat provides additional useful information about the request itself such asrequestId - The contents of both
extensionsfields may be subject to change in the future releases of GraphQL API.
Standard Error Codes
Spire provides standard error codes similar to the HTTP error codes where each error code indicates a specific class of errors.
GRAPHQL_PARSE_FAILED- The GraphQL operation string contains a syntax error.
GRAPHQL_VALIDATION_FAILED- The GraphQL operation is not valid against the server’s schema.
BAD_USER_INPUT- The GraphQL operation includes an invalid value for a field argument. Error with this code most commonly occurs:
- Arguments have incorrect type. For example
mmsiwas submitted as a string instead of an integer. - Validation failed on the value. For example WKT strings contain syntax errors.
- Impossible to perform an operation for given arguments. For example, it is impossible to calculate routes for given arguments.
- Arguments have incorrect type. For example
UNAUTHENTICATED- The server failed to authenticate a user. For example when the
Authorizationheader doesn’t present in the request. FORBIDDEN- Query contains a request to the data which is not authorized by the provided token. For example when you are trying to query vessel characteristics but you don’t have access to it.
TIMEOUT_ERROR- Query result didn’t come within the timeout limit.
CLIENT_CLOSED_REQUEST- This error indicates that request was closed by the calling party on the fly and wasn’t fully completed
SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE- One of our services is temporarily unavailable due to some (network) issues. This error code is analogue of HTTP 503 Service Unavailable code and customers might try to retry in this case.
TOO_MANY_REQUESTS- The request was rate-limited. This error is added alongside with response in case it was rate-limited by the GraphQL server.
INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR
- An unspecified error occurred.
Node: the list of error codes is subject to change in the future releases of GraphQL API. Some codes may be added or removed.
Troubleshooting
GRAPHQL_PARSE_FAILEDorGRAPHQL_VALIDATION_FAILEDplease check the correctness of the GraphQL query. You can easily do it in the playground.UNAUTHENTICATEDplease verify your authentication token. Please, check if your token is correct and valid.FORBIDDENthe query contains access to non-authorized parts of the schema.BAD_USER_INPUTplease check the query arguments. Be sure that argument variables for scalars has correct format.TIMEOUT_ERRORorSERVICE_UNAVAILABLEyou may try to retry requestINTERNAL_SERVER_ERRORplease communicate it with the query andrequestIdto the Data Operations team for investigation.TOO_MANY_REQUESTSplease adjust the request rate per minute. See rate limiting.
Rate limiting
To prevent DDoS attacks to Spire API and handle load gracefully we implemented query rate limiting using Leaky Bucket Algorithm algorithm.
Each request that goes to api.spire.com/graphql is being rate limited according to the available quota:
- If the quota is not yet exceeded, then the response will be returned as soon as it’s processed by the Spire API without any limitations.
- If the quota was already exceeded, the processing of the request will be delayed. When request finally got processed the client will receive response alongside with the
TOO_MANY_REQUESTSerror. - Quota gains back as soon as time goes according to moving time window.
- If the request is waiting for too long in the rate limiter queue it will timeout eventually. In this case client will receive empty response alongside with the
TIMEOUT_ERRORerror.
The current request quota is up to 60 requests per minute per token.
We expect our customers wont be affected by the rate limiter unless they are doing a lot of parallel requests with the same token. If you are querying spire API sequentially then you likely won’t be affected by the rate limiter at all.
Each non-rate-limited response will contain a requestQuota field in the response’s extensions with data about the remaining quota to allow customers to adjust the request rate before making the next request.
{
"data": { ... },
"extensions": {
"requestQuota": {
"limit": "60 req/m (burst 60)",
"remaining": 59
}
}
}Where:
- limit
- textual description of current rate limiter policy.
- remaining
- number of requests per minute left for current quota.
Reaching0indicates the query was rate-limited.
Rate limiting multi-root queries
Requests with multi-root queries are treated as several independent requests from the rate limiter perspective.
Each root query executed in parallel and represented independent self-sufficient request to our underlying infrastructure.
For example, the following query will be counted as 2 standalone queries:
{
tankers: vessels(shipType: [TANKER_CRUDE, TANKER_PRODUCT, TANKER_CHEMICALS]) {
nodes {
staticData {
mmsi
name
}
}
}
cargo: vessels(shipType: [CONTAINER, GENERAL_CARGO]) {
nodes {
staticData {
mmsi
name
}
}
}
}The rate limiter quota will be decreased by 2 and will look in the following way:
{
"data": {
"tankers": { ... },
"cargo": { ... }
},
"extensions": {
"requestQuota": {
"limit": "60 req/m (burst 60)",
"remaining": 58
}
}
}Best practices
Use gZip compression
The Maritime 2.0 API supports gZip compression of the output. Since JSON payload is mostly text, it compresses exceptionally well with gZip.
You can gain up to 20% reduction in payload size using gZip compression in production.
We encourage our clients to send the header alongside with requests:
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflatecurl --request POST \ ~/Dev/maritime-customer-documentation
--url https://api.spire.com/graphql \
--header 'Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflate' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer ' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{"query":"query{ vessels(first: 99) { nodes{ staticData { name mmsi imo } } } }"}'Query what you need
Unlike REST, where the endpoint defines the resource and the received data, the GraphQL exposes a single endpoint with a global schema where you can query whatever you want.
The ability to define precisely the data you want — and only the data you want — is a powerful advantage over traditional REST API endpoints.
By making focused queries you can focus on data you need and omit unimportant one. If you need just vessel positions, then query for vessel positions and omit everything else. If you need vessel characteristics, then query for vessel positions and omit everything else.
The following example shows the query focused only on getting only positional information about the vessels:
query queryVesselsPositions(
$limit: Int
$after: String
$startTime: DateTime!
$endTime: DateTime!
) {
vessels(
first: $limit
after: $after
lastPositionUpdate: { startTime: $startTime, endTime: $endTime }
) {
pageInfo {
endCursor
hasNextPage
}
nodes {
id
staticData {
mmsi
}
lastPositionUpdate {
timestamp
latitude
longitude
heading
speed
rot
accuracy
course
maneuver
navigationalStatus
}
}
}
}Querying only what you need, along with using gZip compression, could significantly reduce the amount of transferred data and therefore increase the performance.
Tutorials
Setting up an API connection via Python
In this tutorial, we will go through the steps necessary to connect to the Spire Maritime 2.0 API using a sample Python client. With this sample program, you may execute the following queries:
- Return data for all vessels globally
- Return data for a specific MMSI list
- Return data for all vessels in a specified AOI
We recommend using a virtual environment, such as pipenv, when completing this tutorial. Read the instructions to start a Pipenv virtual environment to get started.
Installing the requirements
Once you have the virtual environment running, install the requirements found in the requirements.txt file:
pip3 install -r requirements.txtModify the settings
Next, edit the settings.yaml file to reflect your environment.
Note: all files are assumed to be in the same directory as the program.
Below are descriptions of each variable in the setting file:
endpoint- The URL to the service
token- Authentication token
name_of_gql_query_file- Name of file containing query to execute. Currently there are three: sample_1.txt, sample_2.txt, and sample_3.txt. See descriptions below.
name_of_raw_ouput_file- Name of raw output log. If blank, no log is produced
name_of_csv_file- Name of csv file. If blank, no file is produced
pages_to_process- Max number of pages to process. A helpful setting for debugging. If set to 0, all pages are processed
There are three sample queries provided in the program that are set in the name_of_gql_query_file variable:
- sample_1.txt
- Returns all available Vessel, Voyage, and PositionUpdates fields for all vessels globally
- sample_2.txt
- Returns all available Vessel, Voyage, and PositionUpdates fields for a specific MMSI list
- sample_3.txt
- Returns all available Vessel, Voyage, and PositionUpdates fields for all vessels in a specified AOI (Indian Ocean)
Important Note – pageInfo
This client requires each query to include a section to request pageInfo. For example:
query{
pageInfo {
hasNextPage
endCursor
}
nodes {
id
updateTimestamp
staticData {
imo
(. . .)Creating a new query
To create a custom query, follow the steps below:
- Create a text file (file with .txt extension) in the same folder that you saved the sample python client files in your Pipenv virtual environment.
- Write a query using the samples as a guide (more information about writing queries). Please review the the important note regarding
pageInfoabove. - Edit the settings.yaml file and add the name of the file you created after
name_of_gql_query_file. Example:name_of_gql_query_file: 'my-new_query.txt'
When writing a custom query file, it is important that you do not place any comments or text that does not represent a query in the newly created file.
Run the Program
The run.py program will read the settings.yaml file and execute a query based on the fields listed in the specified file in name_of_gql_query_file variable. To run the program, execute the following code in the virtual environment.
pipenv run python3 run.pyVirtual environment example:
my_virtual_envas the directory containing the Python virtual environmentvessels_v2_graphqlas the directory containing this repository
source my_virtual_env/bin/activate [ENTER]
cd vessels_v2_graphql [ENTER]
python3 run.pyIf you specified the desired name of the CSV file in the name_of_csv_file variable and/or the name of the output log in the name_of_raw_output_file variable, these files can be accessed in your directory once the program completes.
All log information for debugging purposes can be found in the file demo_client.log.
Congratulations! You have successfully executed your first GraphQL query using the Spire Maritime 2.0 API.
The tutorial code is for demonstation purposes and should not be used in production.
The code is not included in a customer support contract unless explicately documented elsewhere.
Available root queries
vessels- Get static vessel data and some enhanced data
portEventsByVessel- Get live and historical port events for a vessel
portEventsByLocation- Get live and historical events for a port
port- Given a UNLOCODE, get port latitude, longitude and name
matchedPort- Given a string such as port name, get the matching port UNLOCODE and other port data
The vessels root query
The vessels root query, also called Vessels 2.0, was designed to return only the most recent information provided for each vessel.
It joins the position reports and static voyage reports which are transmitted in separate AIS messages into a single record, making development more efficient, clean, and clear.
Query arguments
All arguments for the vessels query:
vessels(
after: String
first: Int = 100
areaOfInterest: AreaOfInterest
callsign: [String!]
flag: [String!]
imo: [IMO!]
lastPositionUpdate: TimeRange
lastTimestamp: TimeRange
lastUpdate: TimeRange
mmsi: [MMSI!]
name: [String!]
partialNameSearch: Boolean
shipType: [ShipType!]
): VesselConnection!More information about the GraphQL Object Types of the arguments fields can be found below. All fields should resolve to a scalar type.
Further details about all the fields can be found in the Data Dictionary section.
areaOfInterest
If provided, only vessels with their most recent position being within the area of interest defined by polygon(s) will be returned.
The area of interest is either a GeoJSON object or a WKT string; in either case representing a closed polygon or multiple polygons. It is an error to set both the geoJson and wkt fields, or to leave areaOfInterest filter empty.
polygon- Polygon geometry in GeoJSON format only.
multiPolygon- MultiPolygon geometry in GeoJSON format only.
wkt- Geometry in a Well-Known Text format. This can contain either Polygon or Multiple-Polygons.
NOTE: Users whose service is already restricted to a fixed Area of Interest can only filter within the fixed area or a subset of it.
type AreaOfInterest {
polygon: GeoJsonPolygonInput
wkt: WKT
}query multiPolygon {
vessels(areaOfInterest: {
multiPolygon: {
type: "MultiPolygon",
coordinates: [
[
[
[30,20],
[45,40],
[10,40],
[30,20]
]
],
[
[
[ 15,5],
[40,10],
[10, 20],
[5, 10],
[15, 5]
]
]
]
}
}) {
nodes {
id
staticData {
imo
mmsi
name
}
}
}
}TimeRange
There are 3 TimeRange filters applicable to the vessels query which each use a TimeRange as defined below.
The 3 TimeRange filters are:
lastPositionUpdatewhich filters on the timestamp of when a position update is record in the API system. Note this is different from the position timestamp which is when the AIS position report is transmitted.lastTimestampwhich filters on the timestamp of the last reported AIS message for a vessel.lastUpdatewhich filters on the time when any updated was last made to a vessel.
endTime- Timestamp of the end of the time range (RFC 3339 format); if omitted, the current time is used.
startTime- Timestamp of the beginning of the time range (RFC 3339 format).
type TimeRange {
endTime: DateTime
startTime: DateTime!
}lastPositionUpdate
If provided, only vessels having their most recent position update time within the provided time range will be returned.
Example use of lastPositionUpdate : requesting all vessels with position updates since a specified time
lastPositionUpdate:{
startTime:"2022-08-12T11:00:00.00Z"
}Example use of lastPositionUpdate : requesting all vessels with position updates between specified start and end times
lastPositionUpdate:{
startTime:"2022-08-12T11:00:00.00Z"
endTime:"2022-08-12T11:09:59.99Z"
}lastTimestamp
If provided, only vessels having their most recent AIS message timestamp within the provided time range will be returned.
Example use of lastTimestamp : requesting all vessels where the transmission timestamp of the most recent AIS message is since a specified time
lastTimestamp:{
startTime:"2022-08-12T11:00:00.00Z"
}Example use of lastTimestamp : requesting all vessels where the transmission timestamp of the most recent AIS message is between specified start and end times
lastTimestamp:{
startTime:"2022-08-12T11:00:00.00Z"
endTime:"2022-08-12T11:09:59.99Z"
}lastUpdate
If provided, only vessels having their most recent update time within the provided time range will be returned.
Note: lastUpdate filter is available from 2022-08-30
Example use of lastUpdate – requesting all vessels with updates since a specified time
lastUpdate:{
startTime:"2022-08-12T11:00:00.00Z"
}Example use of lastUpdate – requesting all vessels with updates between specified start and end times
lastUpdate:{
startTime:"2022-08-12T11:00:00.00Z"
endTime:"2022-08-12T11:09:59.99Z"
}shipType
Only return vessels having one of the specified vessel types. ShipType must be specified in all capital letters.
Note: Several shipType values were only reported in Maritime 2.0 after 2022-08-10 and prior to that they were reported as OTHER. Most of these types are smaller, non-IMO vessels with types reported by AIS that are not covered by Spire Vessel Characteristics data.
Valid shipType values are shown below:
ANTI_POLLUTION- Anti Pollution Vessel
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 CAR_CARRIER- Car Carrier
COMBINATION_CARRIER- Combination Carrier
CONTAINER- Container
DIVE_VESSEL- Dive Vessel
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 DREDGER- Dredger
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 DRY_BULK- Dry Bulk Cargo
FISHING- Fishing
GAS_CARRIER- Gas Carrier
GENERAL_CARGO- General Cargo
GENERAL_TANKER- General Tanker
HIGH_SPEED_CRAFT- High Speed Craft
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 LAW_ENFORCEMENT- Law Enforcement
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 LIVESTOCK- Livestock Carrier
LNG_CARRIER- LNG Carrier
MEDICAL_TRANS- Medical Transport
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 MILITARY_OPS- Military Operations
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 OFFSHORE- Offshore Vessel
OTHER- Other
PASSENGER- Passenger
- previously reported as
VEHICLE_PASSENGERup to 2022-08-30 PILOT_VESSEL- Pilot Vessel
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 PLEASURE_CRAFT- Pleasure Craft
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 PORT_TENDER- Port Tender
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 REEFER- Reefer Cargo
ROLL_ON_ROLL_OFF- Roll-on Roll-off Cargo
SAILING- Sailing
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 SEARCH_AND_RESCUE- Search and Rescue
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 SPECIAL_CRAFT- Special Craft
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 TANKER_CHEMICALS- Tanker – Chemicals
TANKER_CRUDE- Tanker – Crude
TANKER_PRODUCT- Tanker – Product Tanker
TUG- Tug
VEHICLE_PASSENGER- Vehicle/Passenger
Output objects
Combined vessel, characteristics, voyage, and position objects.
All values represent the latest information available on the vessel.
More details on the field meanings.
type Vessel {
id: ID!
updateTimestamp: DateTime
staticData: VesselStaticData!
lastPositionUpdate: lastPositionUpdate
currentVoyage: Voyage
characteristics: VesselCharacteristics
}Voyage
type Voyage {
destination: String
draught: Float
eta: DateTime
matchedPort: MatchedPort
timestamp: DateTime
updateTimestamp: DateTime
}MatchedPort
Port matched based on destination.
matchScore is the confidence value of the match and ranges between 0 and 1 .
The match with the highest matchScore is returned.
type MatchedPort {
matchScore: Float!
port: Port
}Port
Matched port with the best confidence value.
type Port {
centerPoint: GeoPoint
name: String!
unlocode: UNLOCODE!
}GeoPoint
Port central point.
type GeoPoint {
latitude: Float!
longitude: Float!
}query getVoyage {
vessels(imo: [9282742]) {
nodes {
staticData {
imo
mmsi
}
currentVoyage {
destination
draught
eta
timestamp
updateTimestamp
matchedPort {
matchScore
port {
unlocode
name
centerPoint {
latitude
longitude
}
}
}
}
}
}
}lastPositionUpdate
Latest vessel position update.
type lastPositionUpdate {
accuracy: AisAccuracy
collectionType: PositionCollectionType
course: Float
heading: Float
latitude: Float
longitude: Float
maneuver: AisManeuverIndicator
navigationalStatus: AisNavigationStatus
rot: Float
speed: Float
timestamp: DateTime
updateTimestamp: DateTime
}AisAccuracy
Vessel position accuracy flag. The position accuracy flag indicates the accuracy of the fix.
enum AisAccuracy {
"Indicates a DGPS-quality fix with an accuracy of < 10ms"
HIGH
"Default accuracy, indicates an unaugmented GNSS fix with accuracy > 10m"
LOW
}PositionCollectionType
Data source of position update.
enum PositionCollectionType {
DYNAMIC
SATELLITE
TERRESTRIAL
}AisManeuverIndicator
Vessel special maneuver indicator.
enum AisManeuverIndicator {
"Special maneuver (such as regional passing arrangement)"
ENGAGED_IN_SPECIAL_MANEUVER
"Not available (default)"
NOT_AVAILABLE
"No special maneuver"
NOT_ENGAGED_IN_SPECIAL_MANEUVER
}AisNavigationStatus
Navigational Status in an AIS message. See our AIS Fundamentals article on how to interpret navigational statuses.
AGROUND- 6 : Aground
AIS_SART_IS_ACTIVE- 14 : Any of the following are active: AIS-SART (Search and Rescue Transmitter), AIS-MOB (Man Overboard), AIS-EPIRB (Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon)
AT_ANCHOR- 1 : Anchored
CONSTRAINED_BY_HER_DRAUGHT- 4 : Ship draught is limiting its movement
ENGAGED_IN_FISHING- 7 : Engaged in fishing
MOORED- 5 : Moored (tied to another object to limit free movement)
NOT_DEFINED_DEFAULT- 15 : Undefined (default)
NOT_UNDER_COMMAND- 2 : Not under command
POWER_DRIVEN_VESSEL_PUSHING_AHEAD_TOWING_ALONGSIDE- 12 : Power-driven vessel pushing ahead/towing alongside
POWER_DRIVEN_VESSEL_TOWING_ASTERN- 11 : Power-driven vessel towing astern
RESERVED_FOR_FUTURE_AMENDMENT_OF_NAVIGATIONAL_STATUS_FOR_HSC- 9 : Number reserved for modifying reported status of ships carrying dangerous goods/harmful substances/marine pollutants
RESERVED_FOR_FUTURE_AMENDMENT_OF_NAVIGATIONAL_STATUS_FOR_WIG- 10 : Number reserved for modifying reported status of ships carrying dangerous goods/harmful substances/marine pollutants
RESERVED_FOR_FUTURE_USE- 13 : Reserved for future use
RESTRICTED_MANEUVERABILITY- 3 : Has restricted maneuverability
UNDER_WAY_SAILING- 8 : Under way sailing
UNDER_WAY_USING_ENGINE- 0 : Under way using its engine
VesselStaticData
Vessel static information.
type VesselStaticData {
aisClass: AisClass
callsign: String
dimensions: VesselDimensions
flag: String
imo: IMO
mmsi: MMSI
name: String
shipSubType: ShipSubType
shipType: ShipType
timestamp: DateTime
updateTimestamp: DateTime
validated: VesselValidatedStaticData
}AisClass
Vessel AIS class, A or B.
enum AisClass {
"AIS information from a class A transponder"
A
"AIS information from a class B transponder"
B
}VesselDimensions
Vessel Dimensions.
type VesselDimensions { a: Int b: Int c: Int d: Int length: Int width: Int }
VesselValidatedStaticData
Note: VesselValidatedStaticData was released in November 2023.
type VesselValidatedStaticData {
imo: IMO
name: String
callSign: String
shipType: ShipType
dimensions: { width: int length: int }
}
ShipSubType
Subtype of the ship and cargo. Valid values are listed below:
AGGREGATES_CARRIER- General Cargo: Aggregates Carrier
ALUMINIUM_CARRIER- Dry Bulk: Aluminium Carrier
BITUMEN_CARRIER- General Cargo: Bitumen Carrier
CABU_CARRIER- Dry Bulk: Bulk/Caustic Soda Carrier (CABU)
CARBON_DIOXIDE- General Tanker: Carbon Dioxide Tanker
CAR_CARRIER- Car Carrier
CEMENT_CARRIER- Dry Bulk: Cement Carrier
COAL- Dry Bulk: Coal Carrier
COMBINATION_CARRIER- Combination Carrier
CONTAINER- Container
CONTAINER_BULK- Dry Bulk: Container Bulk Carrier
CONTAINER_REEFER- Container: Reefer
DECK_CARGO- General Cargo: Deck-Cargo
DRY_BULK- Dry Bulk: Dry Bulk Carrier
EFFLUENT_TANKER- General Tanker: Effluent Tanker
FISHING- Fishing
FISH_CARRIER- General Cargo: Fish Carrier
GENERAL_TANKER- General Tanker
GREAT_LAKES- Dry Bulk: Great Lakes Carrier
GYPSUM_CARRIER- Dry Bulk: Gypsum Carrier
HEAVY_LIFT- General Cargo: Heavy Lift
HEAVY_LIFT_SEMI_SUBMERSIBLE- General Cargo: Heavy Lift – Semi Submersible
LIMESTONE_CARRIER- Dry Bulk: Limestone Carrier
LIVESTOCK- Livestock Carrier
LNG_CARRIER- LNG Carrier: LNG Carrier
LOGS- General Cargo: Logs
LOG_CARRIER- Dry Bulk: Log Carrier
LPG_CARRIER- Gas Carrier: LPG Carrier
LUMBER_CARRIER- Dry Bulk: Lumber Carrier
MISCELLANEOUS- General Cargo: Miscellaneous
MOLASSES_CARRIER- General Tanker: Molasses Carrier
MULTI_PURPOSE_CARRIER- General Cargo: Multi-purpose Carrier
null- No vessel subtype
NUCLEAR_FUEL_CARRIER- General Cargo: Nuclear Fuel Carrier
OFFSHORE- Offshore Vessel
OPEN_HATCH- Dry Bulk: Open Hatch Carrier
ORE_BULK_OIL_CARRIER- Combination Carrier: Ore/Bulk/Oil Carrier
ORE_CARRIER- Dry Bulk: Ore Carrier
ORE_OIL_CARRIER- Combination Carrier: Ore/Oil Carrier
OTHER- Other
PALLET_CARRIER- General Cargo: Pallet Carrier
PROBO- General Tanker: PROBO Tanker
REEFER- Reefer Cargo
REPLENISHMENT- General Tanker: Replenishment
ROLL_ON_ROLL_OFF- General Cargo: Roll-on Roll-off
SEA_RIVER_TYPE- General Cargo: Sea River Type
SELF_DISCHARGING- Self Discharging
SLOPS- General Tanker: Slops
STONE_CARRIER- General Cargo: Stone Carrier
TANKER_CHEMICALS- Tanker – Chemicals
TANKER_CRUDE- Tanker – Crude
TANKER_PRODUCT- Tanker – Product Tanker
TUG- Tug
TWEEN_DECKER- General Cargo: Tween Decker
VEG_OIL_CARRIER- General Tanker: Vegetable Oil Carrier
VEHICLE_PASSENGER- Vehicle/Passenger
WATER_CARRIER- General Tanker: Water Carrier
WINE_CARRIER- General Tanker: Wine Carrier
WOOD_CHIP_CARRIER- Dry Bulk: Wood Chip Carrier
WOOD_PULP- Dry Bulk: Wood Pulp Carrier
ShipType
Only return vessels having one of the provided vessel types.
ShipType must be specified in all capital letters.
Note: Several shipType values were only reported in Maritime 2.0 after 2022-08-10 and prior to that they were reported as OTHER. Most of these types are smaller, non-IMO vessels with types reported by AIS that are not covered by Spire Vessel Characteristics data.
Valid shipType values are shown below:
ANTI_POLLUTION- Anti Pollution Vessel
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 CAR_CARRIER- Car Carrier
COMBINATION_CARRIER- Combination Carrier
CONTAINER- Container
DIVE_VESSEL- Dive Vessel
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 DREDGER- Dredger
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 DRY_BULK- Dry Bulk Cargo
FISHING- Fishing
GAS_CARRIER- Gas Carrier
GENERAL_CARGO- General Cargo
GENERAL_TANKER- General Tanker
HIGH_SPEED_CRAFT- High Speed Craft
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 LAW_ENFORCEMENT- Law Enforcement
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 LIVESTOCK- Livestock Carrier
LNG_CARRIER- LNG Carrier
MEDICAL_TRANS- Medical Transport
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 MILITARY_OPS- Military Operations
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 OFFSHORE- Offshore Vessel
OTHER- Other
PASSENGER- Passenger
- previously reported as
VEHICLE_PASSENGERup to 2022-08-30 PILOT_VESSEL- Pilot Vessel
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 PLEASURE_CRAFT- Pleasure Craft
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 PORT_TENDER- Port Tender
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 REEFER- Reefer Cargo
ROLL_ON_ROLL_OFF- Roll-on Roll-off Cargo
SAILING- Sailing
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 SEARCH_AND_RESCUE- Search and Rescue
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 SPECIAL_CRAFT- Special Craft
- previously reported as
OTHERup to 2022-08-30 TANKER_CHEMICALS- Tanker – Chemicals
TANKER_CRUDE- Tanker – Crude
TANKER_PRODUCT- Tanker – Product Tanker
TUG- Tug
VEHICLE_PASSENGER- Vehicle/Passenger
pageInfo
Information about pagination in a connection.
type PageInfo {
endCursor: String
hasNextPage: Boolean!
}totalCount
Information about the amount of results in a query. The indicated value might be a lower bound if the total isn’t known when there are too many results.
type ResultCount {
relation: ResultCountRelation!
value: Int!
}ResultCountRelation
enum ResultCountRelation {
EQUAL
LOWER_OR_EQUAL
}Validated Static Data
Recognising that AIS messages can sometimes report incorrect or missing information for vessels, Spire Maritime uses its database of researched Vessel Characteristics (VC) information to report what we consider to be validated values for key information.
Validated values are available for a vessel’s name, imo, callsign, width, length and shipType. They are returned from the VC database when we are confident that a vessel can be identified correctly, and included in a new validated section of the staticData query response. The validated values will often be the same as those reported by the vessel in it’s AIS messages but sometimes will be different, and will be those from the VC database. Note that matching to VC data, and returning of validated values, is only applicable to vessels with IMO numbers and those reporting AIS using class A AIS.
Also, when running API calls that are filtered on a vessel’s imo, name or callsign , if the staticData.validated data is matched by the parameters of the API call, the entry will be included in the API call results (even if the non-validated data does not match).
One of the most valuable use cases of this feature is the recognition of a vessel’s correct imo number when either the wrong IMO or no IMO number is being reported by the vessel in its AIS messages.
Below is an example output of a Maritime 2.0 GraphQL vessels query, correcting the IMO number returned by AIS – the query to obtain this result can be found on the right:
Available fields
- callsign:
String - Validated vessel call sign
- callsignTimestamp:
DateTime - Timestamp when validated callsign was last updated in Vessel Characteristics
- dimensions:
VesselValidatedDimensions - Validated vessel dimensions (width and height)
- imo:
IMO - Validated vessel IMO
- name:
String - Validate vessel name
- nameTimestamp:
DateTime - Timestamp when validated name was last updated in Vessel Characteristics
- shipType:
ShipType - Validated vessel ship type
query VslIMO {
vessels( imo:9250995 lastUpdate : {startTime:"2023-07-01T00:00:00Z" } ) {
nodes {
id
staticData {
name
imo
mmsi
aisClass
callsign
flag
shipType
updateTimestamp
dimensions {
length
width
}
validated {
name
imo
callsign
shipType
dimensions {
length
width
}
}
}
}
}
}
{
"data": {
"vessels": {
"nodes": [
{
"id": "4db14c7d-0728-3b4f-845c-36c02f671b73",
"staticData": {
"name": "DIMITRA C",
"imo": 92500995,
"mmsi": 256058000,
"aisClass": "A",
"callsign": "9HA3802",
"flag": "MT",
"shipType": "CONTAINER",
"updateTimestamp": "2023-07-24T04:37:24.675Z",
"dimensions": {
"length": 294,
"width": 40,
},
"validated": {
"name": "DIMITRA C",
"imo": 9250995,
"callsign": "9HA3802",
"shipType": "CONTAINER",
"dimensions": {
"length": 294,
"width": 40
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
Vessel characteristics
NOTE: Basic characteristics are available to all customers. Extended characteristics are available through an additional licensing.
All Vessel Characteristics data fields and their meanings can be found in the Vessel Characteristics data dictionary and in the Spire Maritime product page for Vessel Characteristics.
type VesselCharacteristics {
basic: VesselCharacteristicsBasic
extended: VesselCharacteristicsExtended
}VesselCharacteristicsBasic
type VesselCharacteristicsBasic {
capacity: VesselCapacityBasic
history: VesselHistoryBasic
vesselTypeAndTrading: VesselTypeAndTradingBasic
}VesselCapacityBasic
type VesselCapacityBasic {
deadweight: Int
grossTonnage: Int
}VesselHistoryBasic
type VesselHistoryBasic {
builtYear: Int
}VesselTypeAndTradingBasic
type VesselTypeAndTradingBasic {
vesselSubtype: String
}VesselCharacteristicsExtended
type VesselCharacteristicsExtended {
capacity: VesselCapacityExtended
design: VesselDesignExtended
dimensions: VesselDimensionsExtended
history: VesselHistoryExtended
propulsion: VesselPropulsionExtended
registration: VesselRegistrationExtended
vesselTypeAndTrading: VesselTypeAndTradingExtended
bunker: VesselBunker
}VesselCapacityExtended
type VesselCapacityExtended {
deadweight: Int
tpcmi: Float
grossTonnage: Int
netTonnage: Int
displacement: Int
liquidCubic98Percent: Int
grainCubicCapacity: Int
teu: Int
holdCount: Int
holdDimensions: String
hatchCount: Int
hatchDimensions: String
feu: Int
teuSurplus: Int
teu14t: Int
laneMeters: Int
cars: Int
passengers: Int
reeferCubic: Int
}VesselDesignExtended
type VesselDesignExtended {
isCoated: Boolean
isGearless: Boolean
isSelfUnloading: Boolean
gearDisplay: String
gearMaxSwl: Float
reeferPointCount: Int
hullTypeCode: String
}VesselDimensionsExtended
type VesselDimensionsExtended {
draught: Float
lengthOverall: Float
airDraught: Float
keelToManifold: Float
depth: Float
beamMoulded: Float
berthCount: Int
}VesselHistoryExtended
type VesselHistoryExtended {
vesselNameDate: DateTime
builtYear: Int
deadYear: Int
shipBuilder: String
hullNumber: String
registeredOwner: String
commercialOwner: String
keelLaidYear: Int
launchYear: Int
}VesselPropulsionExtended
type VesselPropulsionExtended {
mainEngineCount: Int
mainEngineDesigner: String
propulsionType: String
engineDesignation: String
mcoRpm: Int
mcoKw: Int
mcoHp: Int
propellerCount: Int
propellerType: String
bowThrusterCount: Int
sternThrusterCount: Int
}VesselRegistrationExtended
type VesselRegistrationExtended {
class1Code: String
class2Code: String
classDetails: String
isIceClassed: Boolean
iceClass: String
certificates: String
}VesselTypeAndTradingExtended
type VesselTypeAndTradingExtended {
vesselSubtype: String
tradingCategoryCode: TradingCategoryCode
tradingStatusCode: TradingStatusCode
}VesselBunker
type VesselBunker {
bunkers: [VesselFuelBunker!]
range: Int
}VesselFuelBunker
type VesselFuelBunker {
capacity: Int
fuelTypeCode: String
fuelUnitCode: String
tankCount: Int
}Vessel to Port ETA
The Vessel to Port ETA output is provided under the predictedRoute field and provides information about the predicted next port of a vessel and the expected route it will take, along with the corresponding calculated ETA. The route and ETA is continuously updated to provide the most accurate ETA possible even when a vessel deviates from the expected route, slows down or otherwise changes its expected behaviour.
Vessels are being tracked along the expected route and its progress is being validated every 15 minutes otherwise the route and ETA are recalculated.
Prediction of next port and calculation of routes and ETAs is carried out for vessels of following criteria:
- IMO
- Only vessels with a valid IMO number are supported
- Underway
- The vessel must be underway to have valid ETA calculation
- shipType
- Vessels of the following shipTypes are supported: CONTAINER, DRY_BULK, GENERAL_CARGO, GENERAL_TANKER, TANKER_CHEMICALS, TANKER_CRUDE, TANKER_PRODUCT, CAR_CARRIER, GAS_CARRIER, LNG_CARRIER, LIVESTOCK, ROLL ON ROLL OFF, REEFER
destinationPort: Port!
Predicted destination port
centerPoint: GeoPoint
Port central point
name: String!
Port name
unlocode: UNLOCODE!
Port UN/LOCODEdistance: Float
The distance (in NM) from the vessel position to the to the destination port (in nautical miles) at the time of route calculation
duration: TimeDuration!
Route duration
eta: DateTime!
Predicted Estimated Time of Arrival (ETA) for the route
timestamp: DateTime!
Timestamp when the route calculation was done
waypoints: Waypoints
Waypoints delineating the predicted route of the vessels to the destination port
- geoJson:
GeoJsonLineString - Linestring Geometry in GeoJson format
- wkt:
WKT! - Linestring Geometry in WKT format
query{
vessels(shipType: CONTAINER) {
nodes {
id
staticData {
timestamp
mmsi
imo
name
shipType
shipSubType
}
lastPositionUpdate {
latitude
longitude
navigationalStatus
}
currentVoyage {
predictedRoute {
eta
destinationPort {
unlocode
name
centerPoint {
latitude
longitude
}
}
waypoints {
wkt
geoJson {
coordinates
}
}
distance
timestamp
updateTimestamp
}
}
}
}
}
Data dictionary
Spire Maritime 2.0 API includes the highest-level information about a ship in our vessels database. The information contained here is a combination of data from AIS messages and external data sources. The records within provide an up-to-date snapshot of the ship when possible.
| Argument / Output | Field | Type or Object Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Argument | after | string | When paging through results, returns the elements in the result set that come after the specified cursor. The value of the after argument can be obtained from pageInfo.endCursor. Read more about cursor-based pagination. |
| Argument | areaOfInterest | AreaOfInterest | The area of interest is either a GeoJSON object or a WKT string; in either case representing a closed polygon. It is an error to set both the geoJson and wkt fields, or to set neither. If provided, only vessels with their most recent position being within the area of interest defined by the polygon will be returned. |
| Argument | polygon | GeoJsonPolygonInput | Polygon geometry in GeoJSON format. |
| Argument | coordinates | GeoJsonPosition | Polygon coordinates in format [[[number, number]...]...] |
| Argument | type | String | Must be “Polygon” |
| Argument | wkt | String | Represents linestring geometry in Well-Known Text |
| Argument / Output | callsign | String | Vessel call sign – Only return vessels having one of the provided call signs. |
| Argument | first | Int | Maximum number of records to return. The default is 100 and valid values are 1–1000. Anything less than 1 is converted to the default. Anything greater than the maximum is converted to the maximum. Due to how matches are collected, the number of records returned may be less than this value even when there are more matches in the total result set. In other words, use only the pageInfo.hasNextPage property in the response metadata to determine whether to fetch more results, do not test whether the number of records returned is less than this value. |
| Argument / Output | flag | string | Only return vessels sailing under one of the provided countries. The countries must be provided as ISO 3166 alpha-2 codes. Flag string must be capitalized in argument. |
| Argument / Output | imo | Int | Vessel unique International Maritime Organization number |
| Argument | lastPositionUpdate | TimeRange | If provided, only vessels having their most recent position update time within the provided time range will be returned. |
| Argument | endTime | DateTime | Timestamp of the end of the time range (ISO 8601 format); if omitted, the current time is used. |
| Argument | startTime | DateTime | Timestamp of the beginning of the time range (ISO 8601 format). |
| Argument / Output | mmsi | Int | Vessel Maritime Mobile Service Identity |
| Argument / Output | name | String | Vessel name. When using this as an argument, the vessel name must be an exact match, but it is case insensitive (meaning the name does not have to be in all capital letters). |
| Argument / Output | partialNameSearch | Boolean | When using this argument and setting the boolean to TRUE the matching function for the name argument will be altered to match on partial names instead of exact name matches. When setting the value to TRUE only one name can be used in the name argument. The default value of partialNameSearch is set to FALSE |
| , Argument / Output | shipType | ShipType | Category of vessel. Only return vessels having one of the provided vessel types. See shipType in the Output section for the ShipType enumeration details. |
| Output | nodes | Vessel | Combined vessel, voyage and position object. All values represent the latest information available for the vessel. See this link for more details on the field meanings. |
| Output | currentVoyage | Voyage | Latest/current vessel voyage |
| Output | id | ID | Spire internal vessel identifier. |
| Output | lastPositionUpdate | lastPositionUpdate | Latest vessel position update. |
| Output | accuracy | AisAccuracy | Vessel position accuracy flag. The position accuracy flag indicates the accuracy of the fix. |
| Output | collectionType | PositionCollectionType | Data source of position update. Three possible values: DYNAMIC, SATELLITE, TERRESTRIAL. |
| Output | course | Float | Vessel course |
| Output | heading | Float | Vessel directional heading (°) |
| Output | latitude | Float | Geographical position – latitude (°) |
| Output | longitude | Float | Geographical position – longitude (°) |
| Output | maneuver | AisManeuverIndicator | Vessel special maneuver indicator. See maneuver in the Output section for the AisManeuverIndicator enumeration details. |
| Output | navigationalStatus | AisNavigationStatus | Navigational Status in an AIS message. See this FAQ for more information: https://faq.spire.com/how-to-interpret-navigational-status. See AisNavigationStatus in the Output section for the AisNavigationStatus enumeration details. |
| Output | rot | Float | Vessel rate of turn (°/min) |
| Output | speed | Float | Vessel speed (knots) |
| Output | timestamp | DateTime | Timestamp of the static or position update (ISO 8601 format). |
| Output | updateTimestamp | DateTime | Timestamp of the update being processed (ISO 8601 format). |
| Output | staticData | VesselStaticData | Vessel static information. |
| Output | aisClass | AisClass | Vessel AIS class, A or B. See AisClass in the Output section for the AisClass enumeration details. |
| Output | dimensions | VesselDimensions | Vessel dimensions |
| Output | a | Int | Antenna distance to bow (meters) |
| Output | b | Int | Antenna distance to stern (meters) |
| Output | c | Int | Antenna distance to port (meters) |
| Output | d | Int | Antenna distance to starboard (meters) |
| Output | length | Int | Vessel length (meters) |
| Output | width | Int | Vessel width (meters) |
| Output | shipSubType | ShipSubType | Subtype of the ship and cargo. See ShipSubType in the Output section for the ShipSubType enumeration details. |
| Output | pageInfo | PageInfo | Information to aid in pagination. |
| Output | endCursor | String | When paginating forwards, the cursor continues. This is a cursor pointing to the last element in nodes. Pass this value to after argument to continue pagination on next page. |
| Output | hasNextPage | Boolean | The hasNextPage property indicates whether there are more results to paginate through. Use the endCursor to page through the next results. |
| Output | totalCount | ResultCount | Indicates how many results match the query. |
| Output | relation | ResultCountRelation | Either EQUAL or LOWER_OR_EQUAL |
| Output | value | Int | Information about the amount of results in a query. The indicated value might be a lower bound if the total isn’t known when there are too many results. |
| Output | destination | String | Reported destination of the vessel as entered by the captain or crew of the vessel |
| Output | draught | Float | Vessel draught expressed in 1/10 meters |
| Output | eta | DateTime | Estimated time of arrival reported by the vessel as entered by the captain or crew of the vessel |
Vessel characteristics data dictionary
VesselCapacity fields
deadweightinteger- The difference between displacement and the empty vessel (lightweight) at any given draught
- Available in
VesselCapacityBasicandVesselCapacityExtended tpcmifloat- Tons per Centimeter Immersion – how many tons are required to increase the draught by 1cm (useful for trying to estimate the volume of cargo onboard)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended grossTonnageinteger- Tonnage measure of vessels based on the moulded volume of internal spaces
- Available in
VesselCapacityBasicandVesselCapacityExtended netTonnageinteger- Vessel net tonnage
displacementinteger- The amount of water (in tons) displaced by the ship.
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended liquidCubic98Percentinteger- The liquid cubic capacity of the cargo tanks when filled to 98% of capacity
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended grainCubicCapacityinteger- Cubic capacity (in cubic meters) of cargo holds for grain (and other loose dry commodities)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended teuinteger- Twentyfoot Equivalent Unit (measurement of container carrying capacity)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended holdCountinteger- No. of holds
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended holdDimensionsstring- Dimensions of holds
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended hatchCountinteger- No. of hatches
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended hatchDimensionsstring- Dimensions of hatches
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended feuinteger- Fortyfoot Equivalent Unit (capacity of containers of that size)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended teuSurplusinteger- Spare TEU capacity
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended teu14tinteger- Capacity for containers of 14 tons (measurement of container carrying capacity)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended laneMetersinteger- Lane meter capacity
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended carsinteger- Car carrying capacity
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended passengersinteger- Passenger capacity
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended reeferCubicinteger- Cubic meter capacity of the refrigerated cargo space
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended
VesselDesign fields
isCoatedboolean- Indicates if the vessel tanks are coated (Yes/No)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended isGearlessboolean- Indicates if the vessel has no lifting gear (Yes/No)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended isSelfUnloadingboolean- Indicates if the vessel is self-unloading (Yes/No)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended gearDisplaystring- Details of lifting gear
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended gearMaxSwlfloat- Safe working load (lifting capacity) of the lifting gear
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended reeferPointCountinteger- No. of plug-in points for refrigerated containers
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended hullTypeCodestring- Indicates if single or double hull or bottom
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended
VesselDimensions fields
draughtfloat- Distance between the waterline and keel
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended lengthOverallfloat- Length overall
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended airDraughtfloat- Distance from the waterline to highest point on vessel
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended keelToManifoldfloat- Distance from the keel to the manifold
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended depthfloat- Depth (from the deck to keel)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended beamMouldedfloat- Beam moulded
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended berthCountinteger- No. of sleeping berths
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended
vesselHistory fields
vesselNameDatedatetime- Date vessel’s name became active (for history of name changes, etc.)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended builtYearinteger- Year the vessel was delivered from the shipyard to its owner
- Available in
VesselCapacityBasicandVesselCapacityExtended deadYearinteger- Year the vessels was broken or lost
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended shipBuilderstring- Name of the ship builder
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended hullNumberstring- Hull number assigned by the shipyard
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended registeredOwnerstring- Registered owner
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended commercialOwnerstring- Commercial owner
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended keelLaidYearinteger- Date keel laid (keel laying is when construction of the vessel begins)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended launchYearinteger- Launch year (year the vessel was launched from the shipyard for sea trials)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended
VesselPropulsion fields
mainEngineCountinteger- Number of main engines
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended mainEngineDesignerstring- Engine designer
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended propulsionTypestring- Propulsion type code
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended engineDesignationstring- Engine design identifier
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended mcoRpminteger- Maximum continuous output in RPM (rotations per minute)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended mcoKwinteger- Maximum continuous output in KW (kiloWatts)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended mcoHpinteger- Maximum continuous output in HP (horsepower)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended propellerCountinteger- Number of propellers
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended propellerTypestring- Propeller type
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended bowThrusterCountinteger- No. of bow thrusters
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended sternThrusterCountinteger- No. of stern thrusters
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended
VesselRegistration fields
class1Codestring- The name of the classification society who inspects the vessel and awards statutory certificates
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended class2Codestring- The name of the secondary classification society who certificates dual classed vessels
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended classDetailsstring- Vessel class details
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended isIceClassedboolean- Indicates if the vessel is ice classed (Yes/No)
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended iceClassstring- Ice class type
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended certificatesstring- Details of any certificates issued
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended
VesselTypeAndTrading fields
vesselSubTypestring- Specific subtype of vessel
- Available in
VesselCapacityBasicandVesselCapacityExtended tradingCategoryCodeTradingCategoryCode- Identifies if a vessel is In Service, Dead or Newbuilding
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended tradingStatusCodeTradingStatusCode- Vessel trading status
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended
VesselBunker fields
bunkersarray of VesselFuelBunker- Array containing one or multiple bunker (fuel tank) characteristics. Contains the following information for each available bunker:
capacityinteger: Bunker (fuel tank) capacityfuelTypeCodestring: Bunker fuel type. Possible values include:- MGO (Marine gas oil): Roughly equivalent to no. 2 fuel oil, made from distillate only
- MDO (Marine diesel oil): Roughly equivalent to no. 3 fuel oil, a blend of heavy gasoil that may contain very small amounts of black refinery feed stocks, but has a low viscosity up to 12 cSt so it need not be heated for use in internal combustion engines
- IFO (Intermediate fuel oil): Roughly equivalent no. 4 fuel oil, a blend of gasoil and heavy fuel oil, with less gasoil than marine diesel oil
- HFO (Heavy fuel oil): Pure or nearly pure residual oil, roughly equivalent to no. 5 and no. 6 fuel oil
- NSFO (Navy special fuel oil): Another name for no. 5 HFO
- MFO (Marine fuel oil): Another name for no. 6 HFO
fuelUnitCodestring: Bunker fuel unit (e.g. tonnes, litres)tankCountinteger: Number of bunker fuel tanks
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended rangeinteger- Sailing range of the vessel assuming full fuel tanks
- Available in
VesselCapacityExtended
Quickstart kit - vessels
Get started by copying, editing (remove unnecessary fields, change example arguments), and using these Maritime 2.0 request bodies. Each is presented here in fully formatted JSON for legibility; though, this formatting is not required in actual usage.
query {
query_name: vessels(
mmsi: [372934000,477652300,477056400]
imo: [9335173,9516428,9334923]
name: ["COSCO BOSTON","COSCO ENGLAND","COSCO OCEANIA"]
callsign: ["3ELF2","VRML8","VRDQ5"]
shipType: [CONTAINER,DRY_BULK]
flag: ["PA","HK"]
lastTimestamp:{
startTime:"2023-03-01T12:00:00.00Z"
endTime:"2023-03-01T23:59:59.00Z" #optional
}
lastUpdate:{
startTime:"2023-03-01T00:00:00.00Z"
endTime:"2023-03-01T23:59:59.00Z" #optional
}
lastPositionUpdate:{
startTime:"2023-03-01T00:00:00.00Z"
endTime:"2023-03-01T23:59:59.00Z" #optional
}
areaOfInterest:{
polygon:{ #GeoJSON example
type:"Polygon"
coordinates:[
[
[-130.2018527535319,36.178716438196346],
[-133.424291441762,31.52165477752115],
[-122.92259393101197,28.00084022579476],
[-114.49246414840994,29.58924671251927],
[-118.11770767266884,34.867432471412144],
[-130.2018527535319,36.178716438196346]
]
]
}
}
after: "ZTAyODg0Yzkt..." #endCursor from previous call
first: 100
)
{
nodes {
id
staticData {
name
}
}
}
}
query {
query_name: vessels(
first: 10
)
{
pageInfo { #pagination details
hasNextPage
endCursor
}
totalCount { #recordset details
value
relation
}
nodes {
id
staticData {
imo
mmsi
flag
name
callsign
timestamp
shipType
dimensions {
a
b
c
d
width
length
}
}
lastPositionUpdate {
collectionType
course
heading
latitude
longitude
navigationalStatus
rot
speed
timestamp
updateTimestamp
}
currentVoyage {
destination
draught
eta
timestamp
}
characteristics {
basic {
capacity {
deadweight
grossTonnage
}
history {
builtYear
}
vesselTypeAndTrading {
vesselSubtype
}
}
}
}
}
}
query {
query_name: vessels(
first:10
shipType:[CONTAINER]
)
{
nodes {
staticData {mmsi}
characteristics {
extended {
capacity {
deadweight
tpcmi
netTonnage
grossTonnage
displacement
liquidCubic98Percent
grainCubicCapacity
teu
holdCount
holdDimensions
hatchCount
hatchDimensions
feu
teuSurplus
teu14t
laneMeters
cars
passengers
reeferCubic
}
design {
isCoated
isGearless
isSelfUnloading
gearDisplay
gearMaxSwl
reeferPointCount
hullTypeCode
}
dimensions {
draught
lengthOverall
airDraught
keelToManifold
depth
beamMoulded
berthCount
}
history {
vesselNameDate
builtYear
deadYear
shipBuilder
hullNumber
registeredOwner
commercialOwner #available from 2022-01-26
keelLaidYear
launchYear
}
propulsion {
mainEngineCount
mainEngineDesigner
propulsionType
engineDesignation
mcoRpm
mcoKw
mcoHp
propellerCount
propellerType
bowThrusterCount
sternThrusterCount
}
registration {
class1Code
class2Code
classDetails
isIceClassed
iceClass
certificates
}
vesselTypeAndTrading {
vesselSubtype
tradingCategoryCode
tradingStatusCode
}
bunker {
bunkers {
capacity
fuelTypeCode
fuelUnitCode
tankCount
}
range
}
}
}
}
}
}
query {
vessels(mmsi: [] imo: [] name: [] callsign: [] shipType: [] flag: []
lastTimestamp:{startTime:"" endTime:""}
lastUpdate:{startTime:"" endTime:""}
lastPositionUpdate:{startTime:"" endTime:""}
areaOfInterest:{polygon:{type:"Polygon" coordinates:[[]]}}
after: ""
first: 100)
{nodes {id staticData{name}}}
}
query {
vessels( first: 10)
{ pageInfo {hasNextPage endCursor}
totalCount {value relation}
nodes {id
staticData {imo mmsi flag name callsign timestamp shipType dimensions {a b c d width length}}
lastPositionUpdate {collectionType course heading latitude longitude navigationalStatus rot speed timestamp updateTimestamp}
currentVoyage {destination draught eta timestamp}
characteristics {basic {capacity {deadweight grossTonnage} history {builtYear} vesselTypeAndTrading {vesselSubtype}}}
}
}
}
query {
vessels(first:10 shipType:[CONTAINER])
{
nodes {staticData {mmsi}
characteristics {extended {
capacity {deadweight tpcmi netTonnage grossTonnage displacement liquidCubic98Percent grainCubicCapacity teu holdCount holdDimensions hatchCount hatchDimensions feu teuSurplus teu14t laneMeters cars passengers reeferCubic}
design {isCoated isGearless isSelfUnloading gearDisplay gearMaxSwl reeferPointCount hullTypeCode}
dimensions {draught lengthOverall airDraught keelToManifold depth beamMoulded berthCount}
history {vesselNameDate builtYear deadYear shipBuilder hullNumber registeredOwner commercialOwner keelLaidYear launchYear}
propulsion {mainEngineCount mainEngineDesigner propulsionType engineDesignation mcoRpm mcoKw mcoHp propellerCount propellerType bowThrusterCount sternThrusterCount}
registration {class1Code class2Code classDetails isIceClassed iceClass certificates}
vesselTypeAndTrading {vesselSubtype tradingCategoryCode tradingStatusCode}
bunker {bunkers {capacity fuelTypeCode fuelUnitCode tankCount} range}}}
}
}
}
Port Events
With the Port Events API you can monitor live and historical (going back up to 6th September 2022) vessel arrival and departure times in ports, anchorages, terminals and canals. Port Events are captured for the aforementioned locations and all vessel types.
There are two root queries for port events that can be called. The queries are as follows:
portEventsByVessel- Get open/closed/all port events for specific vessel, in provided locations and time range
portEventsByLocation- Get open/closed/all port events in specific location, for provided ships or ship types and time range
portEventsByShipType- Get open/closed/all port events for a specific shipType, for provided time range or last 24 hours
The GraphQL Playground can be used to navigate the documentation and see the full definition of input and output types.
The portEventsByVessel root query
The portEventsByVessel query is able to provide port events for a given vessel. One vessel can be queried at a time and filters can be applied to narrow down the result.
In order to the get the best result for a request, it is recommended to be as specific as possible with the query. The best way to do that is to use any of the available filters if applicable. In the provided example on the right the past events for a set time range for a specific type of location are requested. This would provide a more coherent history of the vessels previous ports by filtering out events from other locations such as anchorage and terminal events with each of the ports.
query { portEventsByVessel(
vessel: {
mmsi: 244150617
}
locations: {
locationType: [PORT]
}
timeRange: {
startTime: "2022-10-21T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2022-10-28T23:59:59Z"
}
state: CLOSED
)
{
...
}
The portEventsByLocation root query
The portEventsByLocation query is able to provide port events for a given location. One location can be queried at a time and filters can be applied to narrow down the result.
For the location query especially, it is recommended to use filters and be as specific as possible in the query to get the desired result. As port events for all vessel and location types are captured it is advisable to use the the shipType filter when querying a location for events of cargo vessels to exclude e.g. pilot vessels, tug boats etc. that might not be of concern. Similarly when querying for all vessels in port the location type should be specified to PORT to exclude all the separate terminal events.
query { portEventsByLocation(
location: {
unlocode: "NLRTM",
locationType: ANCHORAGE
}
vessels: {
shipType: [GAS_CARRIER,TANKER_CHEMICALS]
}
timeRange: {
startTime: "2022-01-28T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2022-09-10T23:59:59Z"
}
state: CLOSED
) {
...
}The portEventsByShipType root query
The portEventsByShipType query is able to provide port events for a given type of vessels. One shipType can be queried at a time and filters can be applied to narrow down the result.
The shipType query allows broader queries to get events for all ships of a certain type in all ports globally and can be used to track in more frequent intervals all events for e.g. CONTAINER vessels without having to indicate specific vessels or ports in the query. The returned data volumes returned by a portEventsByShipType query can be significantly larger than for the portEventsByLocation or portEventsByVessel and care should therefore be taken when defining a time range in the query. To ensure optimal performance, the maximum allowed time range per query is 24 hours. If no time range is specified in the query, data for the last 24 hours will be returned by default.
query { portEventsByShipType(
vessels: {
shipType: GAS_CARRIER
}
timeRange: {
startTime: "2023-01-25T23:00:00Z"
endTime: "2023-01-25T23:59:59Z"
}
state: CLOSED
) {
...
}Querying multiple locations or vessels
While the above queries allow the request for one location or one vessel each, the power of GraphQL can be used to combine queries and get port events for multiple vessels or locations.
For more detailed information see GraphQL Overview Syntax -> Multiple Root Queries. Using GraphQL fragments can help to keep queries easier to read.
As an example you can query port events for ARA (Amsterdam, Rotterdam, Antwerp Range) by combining multiple root queries in one request.
In the example the query looks for:
Locations:
- Port -> NLAMS – Amsterdam
- Port -> NLRTM – Rotterdam
- Port -> BEANR – Antwerp
Vessels
- Gas/Chemical Tankers
- GENERAL_TANKER
- TANKER_PRODUCT
- GAS_CARRIER
- TANKER_CHEMICALS
Date
- 10th November 2022
State
- OPEN – By default all vessels that are currently in port in the ARA range since.
query {
Amsterdam: portEventsByLocation(
location: {
unlocode: "NLAMS",
locationType: PORT
}
vessels: {
shipType: [GENERAL_TANKER, TANKER_PRODUCT, GAS_CARRIER, TANKER_CHEMICALS]
}
timeRange: {
startTime: "2022-11-10T00:00:00Z",
endTime: "2022-11-10T23:59:59Z"
}
) {
totalCount
# ...
}
Rotterdam: portEventsByLocation(
location: {
unlocode: "NLRTM",
locationType: PORT
}
vessels: {
shipType: [GENERAL_TANKER, TANKER_PRODUCT, GAS_CARRIER, TANKER_CHEMICALS]
}
timeRange: {
startTime: "2022-11-10T00:00:00Z",
endTime: "2022-11-10T23:59:59Z"
}
) {
totalCount
#...
}
Antwerp: portEventsByLocation(
location: {
unlocode: "BEANR", locationType: PORT
}
vessels: {
shipType: [GENERAL_TANKER, TANKER_PRODUCT, GAS_CARRIER, TANKER_CHEMICALS]
}
timeRange: {
startTime: "2022-11-10T00:00:00Z",
endTime: "2022-11-10T23:59:59Z"
}
) {
totalCount
# ...
}
}
Query arguments
All arguments for the port events queries:
portEventsByLocation(
location: PortEventsLocationsInput
vessel: PortEventsVesselInput
timeRange: TimeRange
lastUpdate: TimeRange
ataTimeRange: TimeRange
atdTimeRange: TimeRange
state: PortEventStateInput! = OPEN
first: Int = 5000
after: String
): VesselRouteResponsevessel: PortEventsVesselInput
Required when querying portEventsByVessel
portEventsByVessel(
vessel: {
mmsi: 244234000
}
...
)When using portEventsByLocation it can be used as a filter and then needs to be used as an argument called vessels
location: PortEventsLocationsInput
A UNLOCODE is required when querying portEventsByLocation. All the available location types are listed in the Output Objects section type: PortLocationType
portEventsByLocation(
location: {
unlocode: "NLRTM"
locationType: CONTAINER_TERMINAL
} ...
)
When using portEventsByVessel it can be used as a filter and then needs to be used as an argument called locations.
vessel: PortEventsVesselInput
Required when querying portEventsByShipType. All the available ship types are listed here
portEventsByShipType(
vessels: {
shipType: CONTAINER
}
...
)When using portEventsByLocation it can be used as a filter and then needs to be used as an argument within vessels
state: PortEventStateInput
With state the query can be narrowed to down to only get events in a certain state OPEN, CLOSED or ALL.
OPEN- Get events where a vessel has arrived at a location but not yet departed. This can be used e.g. to get vessels currently at a port.
CLOSED- Get events where a vessel has arrived at and departed from a location. This can be used e.g. to get past events.
ALL- Get all events, regardless of whether a vessels has departed from the location or not.
Example for querying vessels currently in port in Rotterdam
portEventsByLocation(
location: {
unlocode: "NLRTM"
}
state: OPEN
...
)TimeRange
There are 4 TimeRange filters applicable to the port events queries which each use a TimeRange as defined below.
The 4 TimeRange filters are:
timeRangewhich filters on the timestamp of when a position update is record in the API system. Note this is different from the position timestamp which is when the AIS position report is transmitted.lastUpdatewhich filters on the timestamp of the last reported AIS message for a vessel.ataTimeRangeis the Actual Time of Arrival time range. With theataTimeRangethe query can be narrowed down to get events where a vessel arrived within the specified TimeRange.atdTimeRangeis the Actual Time of Departure time range. With theatdTimeRangethe query can be narrowed down to get events where a vessel departed within the specified TimeRange.
endTime- Timestamp of the end of the time range (RFC 3339 format); if omitted, the current time is used.
startTime- Timestamp of the beginning of the time range (RFC 3339 format).
portEventsByLocation(
location: {
unlocode: "NLRTM"
}
timeRange: {
startTime: "2022-10-28T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2022-10-28T23:59:59Z"
}
)
Note!
For the portEventsByShipType query the maximum allowed time range is a duration of 24 hours between start and end date.
Output Objects
Available fields in the PortEvent output:
- ata:
DateTime - Actual time of arrival
- atd:
DateTime - Actual time of departure
- draughtAta:
Float - Vessel’s draught at the time of arrival
- draughtAtd:
Float - Vessel’s draught at the time of departure
- draughtChange:
Float - Change in draught
- duration:
TimeDuration - Duration of the port event
- id:
ID - Port event ID
- location:
PortEventLocation! - Port event location
- state:
PortEventState! - Port event state – open or closed
- timestamp:
DateTime - Time when port event was created
- updateTimestamp:
DateTime - Time when port event was last updated
- vessel:
PortEventVesselInfo! - Vessel info at the moment of the event
PortEvent
Both root queries portEventsByVessel and portEventsByLocation return a PortEvent object. The non-standard objects returned in a PortEvent are listed below.
location: PortEventLocation
type PortEventLocation {
centerPoint: GeoPoint
country: String
id: ID!
name: String
type: PortLocationType!
unlocode: UNLOCODE
}
vessel: PortEventVesselInfo
type PortEventVesselInfo {
id: ID!
staticData: PortEventVesselStaticData
}
staticData: PortEventVesselStaticData
type PortEventVesselStaticData {
callsign: String
imo: IMO
mmsi: MMSI
name: String
shipType: ShipType
}
state: PortEventState
- OPEN
- Port events where a vessel has arrived a location and not yet departed.
- CLOSED
- Port events where a vessel has completed its port stay and departed from the location
type: PortLocationType
- PORT
- Port
- ANCHORAGE
- Anchorage
- CONTAINER_TERMINAL
- Container Terminal
- DRY_BULK_TERMINAL
- Dry Bulk Terminal
- GAS_TERMINAL
- Gas Terminal
- GENERAL_CARGO_TERMINAL
- General Cargo Terminal
- LIQUID_BULK_TERMINAL
- Liquid Bulk Terminal
- PASSENGER_TERMINAL
- Passenger Terminal
- ROLL_ON_ROLL_OFF_TERMINAL
- Roll On Roll Off Terminal
- SHIPYARD
- Shipyard
- CANAL
- Canal
Quickstart kit - portEvents
Get started by copying, editing (remove unnecessary fields, change example arguments), and using these Maritime 2.0 request bodies. Each is presented here in fully formatted JSON for legibility; though, this formatting is not required in actual usage.
query {
by_vessel: portEventsByVessel(
vessel: { #mmsi required for portEventsByVessel
mmsi: 372934000
}
locations: {
unlocode: ["NLRTM","USLAX"]
locationType: [PORT, CONTAINER_TERMINAL]
area: {
polygon:{ #GeoJSON example
type:"Polygon"
coordinates:[
[
[-130.2018527535319,36.178716438196346],
[-133.424291441762,31.52165477752115],
[-122.92259393101197,28.00084022579476],
[-114.49246414840994,29.58924671251927],
[-118.11770767266884,34.867432471412144],
[-130.2018527535319,36.178716438196346]
]
]
}
}
}
timeRange: {
startTime: "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2023-03-01T23:59:59Z" #optional
}
lastUpdate: {
startTime: "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2023-03-01T23:59:59Z" #optional
}
ataTimeRange: {
startTime: "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2023-03-01T23:59:59Z" #optional
}
atdTimeRange: {
startTime: "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2023-03-01T23:59:59Z" #optional
}
state: CLOSED
after: "ZTAyODg0Yzkt..." #endCursor from previous call
first: 100
)
{
nodes {
id
location {
name
}
}
}
}
query {
by_location: portEventsByLocation(
location: { #unlocode required for portEventsByLocation
unlocode: "NLRTM"
locationType: [PORT, CONTAINER_TERMINAL] #optional
}
vessels: {
mmsi: [372934000,477652300,477056400]
shipType: [CONTAINER,DRY_BULK]
}
timeRange: {
startTime: "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2023-03-01T23:59:59Z" #optional
}
lastUpdate: {
startTime: "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2023-03-01T23:59:59Z" #optional
}
ataTimeRange: {
startTime: "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2023-03-01T23:59:59Z" #optional
}
atdTimeRange: {
startTime: "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2023-03-01T23:59:59Z" #optional
}
state: ALL
after: "ZTAyODg0Yzkt..." #endCursor from previous call
first: 100
)
{
nodes {
id
location {
name
}
}
}
}
query {
by_shipType: portEventsByShipType(
vessels: { #shipType required for portEventsByShipType
shipType: CONTAINER
}
locations: {
unlocode: ["NLRTM","USLAX"]
locationType: [PORT, CONTAINER_TERMINAL]
area: {
polygon:{ #GeoJSON example
type:"Polygon"
coordinates:[
[
[-130.2018527535319,36.178716438196346],
[-133.424291441762,31.52165477752115],
[-122.92259393101197,28.00084022579476],
[-114.49246414840994,29.58924671251927],
[-118.11770767266884,34.867432471412144],
[-130.2018527535319,36.178716438196346]
]
]
}
}
}
timeRange: {
startTime: "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2023-03-01T23:59:59Z" #optional
}
lastUpdate: {
startTime: "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2023-03-01T23:59:59Z" #optional
}
ataTimeRange: {
startTime: "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2023-03-01T23:59:59Z" #optional
}
atdTimeRange: {
startTime: "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z"
endTime: "2023-03-01T23:59:59Z" #optional
}
state: CLOSED
#after: "ZTAyODg0Yzkt..." #endCursor from previous call
first: 100
)
{
nodes {
id
location {
name
}
}
}
}
query {
query_name: portEventsByLocation(
location: {
unlocode: "NLRTM"
}
state: CLOSED
first: 10
)
{
pageInfo { #pagination details
hasNextPage
endCursor
}
totalCount #recordset details
nodes {
id
timestamp
updateTimestamp
location {
id
name
type
country
unlocode
centerPoint {
longitude
latitude
}
}
vessel {
id
staticData {
mmsi
imo
name
callsign
shipType
}
}
state
ata
atd
duration {
iso
seconds
text
}
draughtChange
draughtAta
draughtAtd
}
}
}
query {
by_vessel: portEventsByVessel(vessel: {mmsi: }
locations: {unlocode: [] locationType: [] area: {polygon:{type:"Polygon" coordinates:[[[]]]}}}
timeRange: {startTime: "" endTime: ""}
lastUpdate: {startTime: "" endTime: ""}
ataTimeRange: {startTime: "" endTime: ""}
atdTimeRange: {startTime: "" endTime: ""}
state:
after: ""
first: 100)
{nodes {id location {name}}}
}
query {
by_location: portEventsByLocation(location: {unlocode: "" locationType: []}
vessels: {mmsi: [] shipType: []}
timeRange: {startTime: "" endTime: ""}
lastUpdate: {startTime: "" endTime: ""}
ataTimeRange: {startTime: "" endTime: ""}
atdTimeRange: {startTime: "" endTime: ""}
state:
after: ""
first: 100)
{nodes {id location {name}}}
}
query {
by_shipType: portEventsByShipType(vessels: {shipType: }
locations: {unlocode: [] locationType: [] area: {polygon:{type:"Polygon" coordinates:[[[]]]}}}
timeRange: {startTime: "" endTime: ""}
lastUpdate: {startTime: "" endTime: ""}
ataTimeRange: {startTime: "" endTime: ""}
atdTimeRange: {startTime: "" endTime: ""}
state:
after: ""
first: 100)
{nodes {id location {name}}}
}
query {
query_name: portEventsByLocation(location: {unlocode: "NLRTM"} first: 10)
{pageInfo {hasNextPage endCursor}
totalCount {value relation}
nodes{id timestamp updateTimestamp
location{id name type country unlocode centerPoint {longitude latitude}}
vessel {id staticData{mmsi imo name callsign shipType}}
state ata atd
duration {iso seconds text}
draughtChange draughtAta draughtAtd
}
}
}
Port Congestion beta
The Port Congestion GraphQL API is a comprehensive data solution that provides real-time and historical insights into port congestion for the commercial maritime industry. By offering granular and high-level metrics, it helps stakeholders identify bottlenecks, monitor port performance, and optimize maritime operations.
Query arguments
Querying the Port Congestion API requires the use of specific parameters to customize data retrieval. A single mandatory argument (port) and two optional arguments (vessels, dateRange) can be specified to fine-tune your data request.
portCongestion(
port: PortCongestionPortInput!
vessels: PortCongestionVesselsInput
dateRange: DateRangeInput
): PortCongestionMetricsport
In the port query parameter, the desired port can be specified for which port congestion data is required. Ports are identified by the UNLOCODE which are used in line with the UNECE UN Location Codes.
portCongestion(
port: {unlocode: "SGSIN"}
...
)
vessels
In the vessel query parameter, the relevant ship type or list of ship types can be specified for which port congestion data is required.
portCongestion(
port: {unlocode: "SGSIN"}
vessels: { CONTAINER }
...
)
Available ship types are all commercial ship types:
- Supported ship types:
- CAR_CARRIER, COMBINATION_CARRIER, GAS_CARRIER, LNG_CARRIER , LIVESTOCK, GENERAL_CARGO, CONTAINER, DRY_BULK, ROLL_ON_ROLL_OFF, REEFER, GENERAL_TANKER, TANKER_CHEMICALS, TANKER_CRUDE, TANKER_PRODUCT, VEHICLE_PASSENGER, PASSENGER
dateRange
In the dateRange query parameter, the desired dateRange can be specified for which port congestion data is required. If no date range is provided, data for the last 24 hours will be returned.
portCongestion(
port: {unlocode: "SGSIN"}
dateRange: {
startDate: "2023-10-08",
endDate: "2023-10-10"
}
...
)
Data Structure
The Port Congestion API is structured hierarchically, starting with the ‘portCongestion’ root query. This root provides access to several metrics, such as ‘congestionIndex’ and ‘vesselsInPort’. Within specific metrics, users can explore detailed data objects, for instance, ‘aggregate’ and ‘byTimeInterval’ associated with the ‘vesselsInPort’ metric. These data objects further encompass a range of statistical attributes, ensuring a comprehensive analysis of each metric.
Example:
In the below example, the average (mean) number of vessels in port for the requested time frame is returned. See the code example on the right?
Example
Below is the code of the illustrated data structure example on the left:
{
portCongestion(
port: { unlocode: "USSAV" }
vessels: { shipType: [CONTAINER] }
) {
vesselsInPort {
aggregate {
mean
}
}
}
}This returns the data as follows:
{
"data": {
"portCongestion": {
"vesselsInPort": {
"aggregate": {
"mean": 6.04166667
}
}
}
}Metrics
Metrics serve as the quantifiable measurements that provide insights into various aspects of port congestion. This section offers a comprehensive breakdown of all available metrics, enabling access and understanding of specific aspects of port operations and shipping behaviours.
- congestionIndex
- A composite metric providing a holistic view of port congestion
- vesselsInPort
- A count of commercial vessels currently located within a specified port’s boundary, available in both historical and real-time data.
- vesselsInAnchorage
- A tally of commercial vessels currently situated in a port’s anchorage areas, indicating the demand for berthing spaces.
- WaitingTimeAtPort
- The duration vessels spend at anchorage before entering the port, differentiated by ship type.
- probabilityOfWaiting
- A ratio indicating the likelihood of a vessel needing to wait in anchorage before docking, derived from comparing vessels having to wait before arrival with direct berthings.
- portTurnaroundTimes
- The time vessels spend within the port’s boundary, broken down by ship type, reflecting port operational efficiency.
{
portCongestion(
port: {unlocode: "NLRTM"}
) {
congestionIndex {
...
}
vesselsInPort {
...
}
vesselsInAnchorage {
...
}
waitingTimeAtPort {
...
vesselsActivity {
probabilityOfWaiting {
...
}
}
}
portTurnaroundTimes {
...
}
}
}
congestionIndex
The Port Congestion Index is a metric developed to provide a comprehensive view of port congestion levels, with the aim of supporting decision-making and improving operational efficiency. This index aggregates several essential port metrics: Vessels in Port, Vessels in Anchorage, Waiting Time at Port, Probability of Waiting, and Port Turnaround Time. To ensure a consistent representation, each of these metrics is normalized. After normalization, weights are assigned to each metric based on their significance. The weighted metrics are then combined to give a clear picture of port congestion. For ease of interpretation, the resultant data is categorized into a traffic-light style format, facilitating its integration into various systems and platforms.
type congestionIndex {
latestValue: PortCongestionIndexValue
byShipType: PortCongestionIndexMetricByShipType
byTimeInterval: PortCongestionIndexMetricByTimeInterval
}Example
What is the congestion index for containerships in Rotterdam now?
{
portCongestion(
port: {unlocode: "NLRTM"},
vessels: {
shipType: [CONTAINER]
}
) {
congestionIndex {
latestValue {
index
level
}
}
}
}
This returns the data as follows:
{
"data": {
"portCongestion": {
"congestionIndex": {
"latestValue": {
"index": 0.20321934,
"level": "LOW_CONGESTION"
}
}
}
}
}vesselsInPort
The Vessels in Port metric provides a count of commercial vessels currently within a specified port polygon area. This data can be historical or real-time, depending on your query parameters. A high Vessels in Port count could signify maximum port capacity utilisation but could also be a precursor to bottlenecks. For example, a sudden uptick in Vessels in Port numbers may necessitate additional logistical planning to avert delays in offloading or reloading cargo.
type vesselsInPort {
latestValue: Int
aggregate: ValueMetricStatistics
byShipType: PortCongestionCountMetricByShipType
byTimeInterval: PortCongestionCountMetricByTimeInterval
}Example
How many containerships are in the port of Savannah right now?
{
portCongestion(
port: { unlocode: "USSAV" }
vessels: { shipType: [CONTAINER] }
) {
vesselsInPort {
latestValue
}
}
}
This returns the data as follows:
{
"data": {
"portCongestion": {
"vesselsInPort": {
"latestValue": 6
}
}
}
}vesselsInAnchorage
The Vessels in Anchorage (VIA) metric counts the number of commercial vessels currently in a port’s anchorage areas. This is vital for gauging the demand for berthing spaces and the potential backlog that may be forming. In a practical sense, a rise in VIA can flag the need for short-term measures, like prioritizing certain vessels based on cargo urgency or rerouting others to alternate anchorages.
type vesselsInAnchorage {
latestValue: Int
aggregate: ValueMetricStatistics
byShipType: PortCongestionCountMetricByShipType
byTimeInterval: PortCongestionCountMetricByTimeInterval
}Example
How many containerships are waiting in the anchorage in Savannah?
{
portCongestion(
port: { unlocode: "USSAV" }
vessels: { shipType: [CONTAINER] }
) {
vesselsInAnchorage {
latestValue
}
}
}
This returns the data as follows:
{
"data": {
"portCongestion": {
"vesselsInAnchorage": {
"latestValue": 10
}
}
}
}waitingTimeAtPort
The Wait Time at Port (WTP) metric provides an aggregated measurement of how long vessels waited at anchorage before entering the port, and it’s often broken down by ship type. This metric uncovers inefficiencies in the transition from anchorage to port, offering insights for operational improvements. For instance, if WTP for container ships is substantially longer than for other vessel types, it may indicate issues at a terminal or general congestion.
type waitingTimeAtPort {
latestValue: Int
aggregate: ValueMetricStatistics
byShipType: PortCongestionCountMetricByShipType
byTimeInterval: PortCongestionCountMetricByTimeInterval
vesselsActivity: WaitAtPortVesselsActivity
}
probailityOfWaiting
The Probability of Waiting is an essential extension of the Wait Time at Port (WTP) metric. Derived from vessel arrivals, this metric indicates the likelihood that a ship will have to wait in anchorage before being able to dock. It’s a dynamic figure obtained by dividing the number of vessels that had to wait in the anchorage before arrival by the total number of arrivals.
For example, consider a day at Port X focusing on container ships:
Total number of vessels arrived: 57
Number of vessels arriving at port coming from the anchorage: 12
Number of vessels arriving directly at port without anchorage waiting: 45
The Probability of Waiting would be 12/57×100=21%
This metric is invaluable for predicting operational flux and guiding short-term logistical decision-making. For instance, a high Probability of Waiting could inform a decision to reduce speed for an approaching vessel to reduce waiting time.
type waitingTimeAtPort {
vesselsActivity {
probabilityOfWaiting: Float
vesselsEnteredPort: Int
vesslesWaitedAtAnchorage: Int
}
Example
How long are containerships waiting before berthing in Savannah? And how likely is it that they have to wait?
{
portCongestion(
port: {unlocode: "USSAV"},
vessels: {shipType: [CONTAINER]}
) {
waitingTimeAtPort {
aggregate {
mean {
text
}
min {
text
}
max {
text
}
}
vesselsActivity {
probabilityOfWaiting
}
}
}
}
This returns the data as follows:
{
"data": {
"portCongestion": {
"waitingTimeAtPort": {
"aggregate": {
"mean": {
"text": "83h36m24s"
},
"min": {
"text": "41h55m18s"
},
"max": {
"text": "126h7m24s"
}
},
"vesselsActivity": {
"probabilityOfWaiting": 0.66666667
}
}
}
}
}portTurnaroundTime
The Port Turnaround Time (PTT) measures the length of time a vessel spends inside the port polygon area, usually also disaggregated by ship type. It serves as a key performance indicator for the port; shorter PTT usually suggests more efficient operations. Consider a scenario where bulk carriers have a shorter PTT in one week and then a sudden uptick in the following week. This could indicate issues with loading gears or other operational impacts such as weather or pilot availabilities.
type waitingTimeAtPort {
latestValue: Int
aggregate: ValueMetricStatistics
byShipType: PortCongestionCountMetricByShipType
byTimeInterval: PortCongestionCountMetricByTimeInterval
}Example
How long are containerships staying in port of Savannah on average?
{
portCongestion(
port: {unlocode: "USSAV"},
vessels: {shipType: [CONTAINER]}
) {
portTurnaroundTime {
aggregate {
mean {
text
}
}
}
}
}
This returns the data as follows:
{
"data": {
"portCongestion": {
"portTurnaroundTime": {
"aggregate": {
"mean": {
"text": "34h38m59s"
}
}
}
}
}
}Data Objects
The data objects provide a variety of views on the data related to the selected metric. The data can be provided either as the ‘latestValue’ available for a metric or the ‘aggregate’ data available for the selected data range.
The data can also be returned broken down into either ‘byShipType’ or ‘byTimeInterval’.
latestValue
Providing the latestValue for a given count metric.
- latestValue
- Returns the most recent value for a given metric as an integer
- PortCongestionIndexValue
- Returns the most recent or requested value of the congestion index
Example
What is the congestion index for containerships in Rotterdam now?
{
portCongestion(
port: {unlocode: "NLRTM"},
vessels: {
shipType: [CONTAINER]
}
) {
congestionIndex {
latestValue {
index
level
}
}
}
}
This returns the data as follows:
{
"data": {
"portCongestion": {
"congestionIndex": {
"latestValue": {
"index": 0.20321934,
"level": "LOW_CONGESTION"
}
}
}
}
}aggregate
Providing aggregated data for the requested date range.
- If no specific ship types are queried, statistics for all types are returned.
- If specific ship types are selected, the aggregate values for those types are returned.
- DurationMetricStatistics
- Returns aggregated duration statistics
- ValueMetricStatistics
- Returns aggregated count statistics
Example
How many containerships are typically in Singapore?
{
portCongestion(
port: { unlocode: "SGSIN" }
vessels: { shipType: [CONTAINER] }
dateRange: {
startDate: "2023-09-01"
endDate: "2023-09-07"
}
) {
vesselsInPort {
aggregate {
mean
median
min
max
range
}
}
}
}
This returns the data as follows:
{
"data": {
"portCongestion": {
"vesselsInPort": {
"aggregate": {
"mean": 41.25,
"median": 41.0,
"min": 33.0,
"max": 50.0,
"range": 17.0
}
}
}
}
}byShipType
Providing results on a per ship type basis for either all ship types or the requested ones in the query.
- PortCongestionCountMetricByShipType
- Returns count metrics, specifically organized by ship type.
- PortCongestionDurationMetricByShipType
- Provides duration metrics, categorized by ship type.
- PortCongestionIndexMetricByShipType
- Delivers the congestion index, segmented by ship type.
Example
What is the highest number of container and dry bulk vessels in Savannah?
{
portCongestion(
port: { unlocode: "USSAV" }
vessels: { shipType: [CONTAINER, DRY_BULK] }
dateRange: {
startDate: "2023-09-01"
endDate: "2023-09-30"
}
) {
vesselsInPort {
byShipType {
shipType
aggregate {
max
}
}
}
}
}
This returns the data as follows:
{
"data": {
"portCongestion": {
"vesselsInPort": {
"byShipType": [
{
"shipType": "CONTAINER",
"aggregate": {
"max": 8.0
}
},
{
"shipType": "DRY_BULK",
"aggregate": {
"max": 5.0
}
}
]
}
}
}
}byTimeInterval
Providing results on a time interval basis meaning the data is returned as time series data for the queried date range giving a value for each day.
- PortCongestionCountMetricByTimeInterval
- Returns count metrics, grouped by a time interval. The default interval is 1 day.
- PortCongestionDurationMetricByTimeInterval
- Offers duration metrics, categorized by the same time interval. The default is 1 day.
- PortCongestionIndexMetricByTimeInterval
- Presents the congestion index, organized by the set time interval.
Example
What is the congestion index for containerships in Rotterdam now?
{
portCongestion(
port: { unlocode: "NLRTM" }
vessels: { shipType: [CONTAINER] }
dateRange: {
startDate: "2023-10-01",
endDate: "2023-10-04" }
) {
congestionIndex {
byTimeInterval {
timeInterval {
endTime
}
value {
index
level
}
}
}
}
}
This returns the data as follows:
{
"data": {
"portCongestion": {
"congestionIndex": {
"byTimeInterval": [
{
"timeInterval": {
"endTime": "2023-10-01T23:59:59.000Z"
},
"value": {
"index": 0.40231769,
"level": "MEDIUM_CONGESTION"
}
},
{
"timeInterval": {
"endTime": "2023-10-02T23:59:59.000Z"
},
"value": {
"index": 0.34812829,
"level": "MEDIUM_CONGESTION"
}
},
{
"timeInterval": {
"endTime": "2023-10-03T23:59:59.000Z"
},
"value": {
"index": 0.38143839,
"level": "MEDIUM_CONGESTION"
}
},
{
"timeInterval": {
"endTime": "2023-10-04T23:59:59.000Z"
},
"value": {
"index": 0.53605895,
"level": "MEDIUM_CONGESTION"
}
}
]
}
}
}
}Statistics
Statistical analysis of the collected data allows for a deeper understanding of the port congestion metrics.
- mean
- The mean, or average, is a measure of central tendency in the data set. It’s beneficial for setting baseline expectations. For example, if the mean waiting time at a port is 12 hours, this can be factored into port operational plans and shipping schedules.
- median
- The median is the middle value of the data set and is less sensitive to outliers than the mean. It’s a solid indicator of a ‘typical’ value. If the median waiting time is 9 hours and the mean is 12 hours, it indicates that a few extended waits skew the mean, whereas the median represents a more common wait time.
- deviation
- Deviation quantifies the variability or spread in the data. A low standard deviation in port turnaround times might suggest consistent port operations, essential information for shippers aiming for punctuality.
- iqr
- The interquartile range (IQR) focuses on the middle 50% of the data, pinpointing where most values are concentrated. If the IQR for waiting times is 4 to 7 hours, it implies that the bulk of ships experience wait times within this window.
- min & max
- These metrics display the extremes in the data set. If the minimum and maximum waiting times are 2 and 22 hours, respectively, it hints at the possible range of wait times ships might encounter.
- range
- The range represents the spread of the data by showing the gap between the maximum and minimum values. A range of 20 hours in waiting times underscores the variation in wait times that vessels might face.
- quantiles
- Quantiles divide the data into equal parts, invaluable for risk evaluations or determining operational thresholds. If the first quantile (Q1) for waiting time is 5 hours, it implies that a quarter of vessels wait no longer than this time.
- percentiles
- Percentiles allow for a detailed breakdown of data distribution. For instance, if a vessel’s waiting time exceeds the 85th percentile, it could indicate the need for further analysis or operational adjustments.
- sampleSize
- Sample size conveys the number of data points used in the analysis. A substantial sample size enhances the trustworthiness of the statistics, reinforcing the basis for data-informed decisions.
The deviation, iqr, quantiles, and some percentiles might not be available for small sample sizes.
Example
How many containerships are typically in Singapore?
{
portCongestion(
port: { unlocode: "SGSIN" }
vessels: { shipType: [CONTAINER] }
dateRange: {
startDate: "2023-09-01"
endDate: "2023-09-07"
}
) {
vesselsInPort {
aggregate {
mean
median
min
max
range
deviation
iqr
quantiles
percentiles {
percentile
value
}
sampleSize
}
}
}
}
This returns the data as follows:
{
"data": {
"portCongestion": {
"vesselsInPort": {
"aggregate": {
"mean": 41.25,
"median": 41.0,
"min": 33.0,
"max": 50.0,
"range": 17.0,
"deviation": 3.30803775,
"iqr": 4.0,
"quantiles": [
39.0,
41.0,
43.0
],
"percentiles": [
{
"percentile": "P_05",
"value": 36.0
},
{
"percentile": "P_10",
"value": 36.5
},
{
"percentile": "P_25",
"value": 39.0
},
{
"percentile": "P_50",
"value": 41.0
},
{
"percentile": "P_75",
"value": 43.0
},
{
"percentile": "P_90",
"value": 45.0
},
{
"percentile": "P_95",
"value": 46.5
}
],
"sampleSize": 168
}
}
}
}
}The matchedPort root query
AIS reported destinations are often non-standard, which leads to difficulty in standardizing and obtaining formatted destination UNLOCODES 0r more granular port information.
You can use the matchedPort root query to try and obtain a normalized port from a non-standard destination text string.
query getMatchedPort{
matchedPort(text: "Sydney"){
matchScore
port{
name
unlocode
}
}
}Query arguments
Obtain port information by supplying search text.
type Query {
matchedPort(text: String!): MatchedPort
}Output
portis described herematchScoreis the confidence value of the match
The match with the highest matchScore is returned
type MatchedPort {
matchScore: Float!
port: Port
}The port root query
You can use the port root query to obtain more information about a specific port, through a provided specific UNLOCODE.
query getPort{
port(unlocode: "USNYC"){
name
unlocode
centerPoint{
latitude
longitude
}
}
}Query arguments
Obtain port information given a UNLOCODE.
The value for unlocode must be a valid value or an error will be returned.
type Query {
port(unlocode: UNLOCODE!): Port
}Output
type Port {
centerPoint: GeoPoint
name: String!
unlocode: UNLOCODE!
}